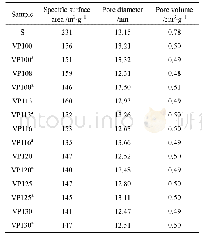
《Table 1 Comparison of BET surface area and photocatalytic hydrogen production rate (HPR) over diffe
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《表面缺陷与钯的沉积对硫化镉纳米晶粒的光催化制氢性能的影响(英文)》
Reaction conditions: 20 mg catalyst; 0.35 mol·L-1 Na2S + 0.25 Na2SO3 as the sacrificial agent; White light(400–800 nm); 2 h; Distance between the reactor and white light was kept at 20 cm; All data were repeated by three times.
We next performed the photocatalytic hydrogen production reaction over above three CdS crystals.Table 1 compares the hydrogen production rate over different catalysts.lr-CdS exhibits the highest photocatalytic activity,with a hydrogen rate of 482μmol h-1·g-1,which is 2.6 times that over sr-CdS(183μmol·h-1·g-1)and 8.8 times that over tp-CdS(55μmol·h-1·g-1).To better study the effect of exposed crystal plane on the activities,we try to normalize hydrogen production rate on a basis of unit surface area to rule out the influence of the surface area.The normalized hydrogen production rates are 6.17,5.10 and 2.78μmol·h-1·m-2 for lrCdS,sr-CdS and tp-CdS,respectively.It is reported that rodlike CdS crystals mainly expose nonpolar surface(100),while the plate-like CdS can expose more 002 surface(polar).In our case,the proportion of nonpolar faces increases with the increase in the aspect ratio from tp-CdS to sr-CdS and to lrCdS.So,the nonpolar surface shows greater contribution to the activity than does the polar surface.However previous work has suggested that the polar surface has higher reactivity than nonpolar one,especially for ZnO in methanol synthesis reaction,photocatalysis,etc.It seems that our results contradict the traditional concept.In combination with the aforementioned PL spectra,we find that the variation of hydrogen production rate show a similar trend as the amount of surface defects(lr-CdS>sr-CdS>tp-CdS).It is speculated that the activity can be associated with the surface defects which may serve as active sites for hydrogen evolution.One may argue that a better crystallization usually results in a higher photocatalytic activity since the defects in the bulk crystal would serve as the sites for the photo-induced charge recombination.A good crystallization often means there are very few lattice defects in the crystal,but this is not much associated with surface defects.The crystallization degree from XRD or TEM cannot actually reflect the degree of surface defects.As we know,surface defects,not perfect surfaces,are required for the chemical adsorption of reactants on a catalyst.It is universally acknowledged that the catalytic activity sites are more often existed in the surface or nearsurface defects because of its high surface unsaturation and high reactivity.
| 图表编号 | XD0043331300 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.02.15 |
| 作者 | 刘志明、刘国亮、洪昕林 |
| 绘制单位 | 武汉大学化学与分子科学学院、武汉大学化学与分子科学学院、武汉大学化学与分子科学学院 |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |