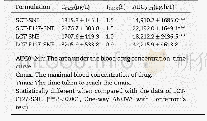
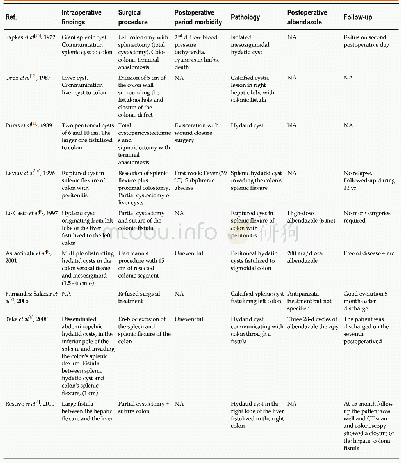
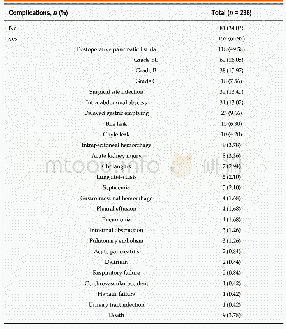
《Table 1 Induction chemotherapy followed by chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced sinonasal undiffe
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《"Induction chemotherapy with docetaxel,cisplatin and fluorouracil followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy for unresectable sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma: Two cases of report"》
1MST represents the duration of survival among the patients receiving induction chemotherapy and chemoradiotherapy.2All patients were classified as Kadish C.3Part of patients received CDDP concomitantly with irradiation.CAV:Cyclophosphamide,doxorubicin an
In unresectable LA-SNUC cases,definitive chemoradiotherapy alone has been widely used[3],but it has shown less promising efficacy than the multimodality treatment that includes surgery[5].The case series showed a poor median overall survival,ranging from 7 to 19 mo,in patients receiving chemoradiotherapy only[2,16,17],which demanded more intensive treatment.A small number of LA-SNUC patients received induction chemotherapy prior to chemoradiotherapy,which is recommended for locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients[18].Chemotherapy with platinum and fluorouracil and subsequent chemoradiotherapy with concomitant cisplatin showed a two-year survival rate of 64%in LA-SNUC patients[12].Considering that most patients had more advanced diseases that were not resectable,the two-year survival rate appeared to be better than that in patients who underwent surgery[11].In order to investigate the efficacy of induction chemotherapy plus chemoradiotherapy,we undertook a review of the literature using PubMed(Table 1).The search terms used were“sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma”and“SNUC”.All SNUC cases published until November 2018 were included in the search.Then,the data of patients receiving induction chemotherapy plus chemoradiotherapy were extracted.Cases in which treatment options or outcomes were not individually described were excluded from the review.Our review highlighted a survival benefit of adding induction chemotherapy to chemoradiotherapy.Compared with the previous cases,our cases showed improved survival.In addition to the effect of the TPF induction chemotherapy,IMRT may contribute to the outcome.IMRT enabled an achievement of steep dose gradients near target volumes,which greatly impacted on a doseresponse relationship in SNUC,and led to a lower rate of radiation-induced toxicity.Retrospective studies indicated the crucial role of IMRT,showing that the use of IMRT was related to longer survival of SNUC patients[10,19].A recently published study also demonstrated the intriguing finding that in patients who responded to induction chemotherapy,definitive chemoradiotherapy provided a better chance of disease control and improved survival than did surgical resection[20],suggesting the possibility that definitive chemoradiotherapy can replace surgery even in resectable LA-SNUC cases.
| 图表编号 | XD0054204500 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.03.26 |
| 作者 | Sho Watanabe、Yoshitaka Honma、Naoya Murakami、Hiroshi Igaki、Taisuke Mori、Hidekazu Hirano、Natsuko Okita、Hirokazu Shoji、Satoru Iwasa、Atsuo Takashima、Ken Kato、Kenya Kobayashi、Fumihiko Matsumoto、Seiichi Yoshimoto、Jun Itami、Narikazu Boku |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Head and Neck Medical Oncology,National Cancer Center Hospital、Department of Head and Neck Medical Oncology,National Cancer Center Hospital、Department of Radiation Oncology,National Cancer Center Hospital、Department of Radiation Oncology,Nat |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1 Induction chemotherapy followed by chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma”的人还看了
-
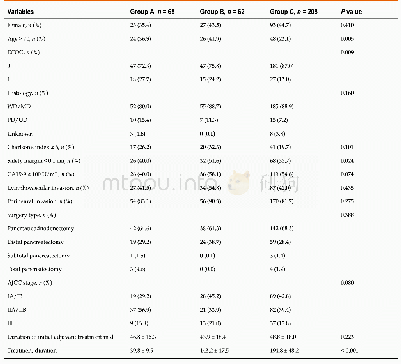
- Table 3 Differences in baseline characteristics between chemotherapy,chemoradiation therapy and chemotherapy plus chemor