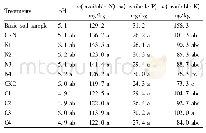
《Table 4–Chemical properties of bauxite residue following different treatments.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Changes in distribution and microstructure of bauxite residue aggregates following amendments addition》
The 3D pore systems for unamended residue exhibited honeycomb structure,whilst longer channels and larger aggregates were discovered in the residues following amendment additions,which indicated that gypsum and vermicompost improved the proportion of water-stable aggregates(Fig.3).Pore parameters of residue aggregates demonstrated that the microstructures of residue aggregates with different treatments showed significant differences.The greatest porosity and the lowest mesoporosity were found in BG1V2,revealing that the combination could accumulate the number of macropores,and may be beneficial to water and nutrient transportation(Table 3).Furthermore,the combination changed the characteristics of pore throat,which may improve the flux of water,gases,and nutrients.Path number was lower in the combination treatment as compared to in gypsum and vermicompost treatments,whilst the combination treatment had the longest paths.The combination treatment decreased the amount of pore throats and the ratio of throat to pore radiusratios,whichindicatedthatgypsumand vermicompost would stimulate water,gas and nutrient fluxes.Compared to gypsum addition,residue aggregates had larger porosity,macroporosity,specific surface area,average length of paths,and average tortuosity of paths following vermicompost addition.These quantitative results revealed that residue aggregate structure improved following amendments addition.It demonstrated that gypsum and vermicompost could stimulate water-stable aggregate formation and enhance pore structure of residue aggregates.Vermicompost was more beneficial to aggregate structure and pore formation,whilst gypsum could change adverse chemical properties and stimulate formation process.It showed that improved structure should enhance leaching of excess soluble salt in the residues and provide a stable soil environment for plant growth,which had been observed in a long-term field rehabilitation trial by Bray et al.(2018).The combined approach(gypsum and organic waste)may be a suitable reclamation strategy on bauxite residue disposal areas.
| 图表编号 | XD0033527300 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.04.15 |
| 作者 | Shengguo Xue、Yuzhen Ye、Feng Zhu、Qiongli Wang、Jun Jiang、William Hartley |
| 绘制单位 | School of Metallurgy and Environment,Central South University、School of Metallurgy and Environment,Central South University、School of Metallurgy and Environment,Central South University、School of Metallurgy and Environment,Central South University、School |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 4–Chemical properties of bauxite residue following different treatments.”的人还看了
-

- Table 2.Carbon and sulfur content and textural property of recovered NiMoS/Al2O3samples following the first runs of HDO