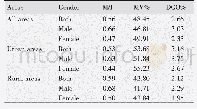
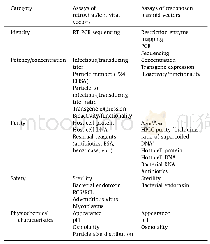
《Table 1Common quality control items of vectors for the gene modification of CAR-T cells.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《CAR-T细胞产品的质量控制和非临床研究——一般原则和关键问题》
At present,the classic approach for sterility test is the 14-day culture method that is described in the pharmacopoeia of most countries.However,since CAR-T cell products often need to be infused into patients shortly after production,alternative quickdetection methods such as gram staining or acridine orange staining are required in process control and release testing.Before a particular quick method is fully validated,two methods must be carried out in parallel.For each batch of cultured CAR-T cells,a sterility test should be performed before the infusion to patients.It is recommended to perform a sterility test on samples taken from culture supernatant at regular intervals after three or four days of culture,covering 48–72 h before release.If contamination is found in the early stages of cell preparation,further preparation should be terminated.Although the results of rapid detection could support product release,it is still necessary to keep track of the14-day culture test and monitor the patient’s condition.Emergency-response solutions must be designed in case the results obtained after cell infusion conflict with the results of the quick release test.Formal procedures are usually required in order to inform the subject’s doctor to identify infected tissues and organs,determine the sensitivity to antibiotics,and carry out the treatment in a timely and effective manner.If the sterility test yields positive results,the production process should be inspected in time,and corresponding corrective/preventive actions(CAPA)should be proposed.
| 图表编号 | XD0061017500 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.02.01 |
| 作者 | 李永红、霍艳、于雷、王军志 |
| 绘制单位 | National Institutes for Food and Drug Control、National Institutes for Food and Drug Control、National Institutes for Food and Drug Control、National Institutes for Food and Drug Control |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1Common quality control items of vectors for the gene modification of CAR-T cells.”的人还看了
-
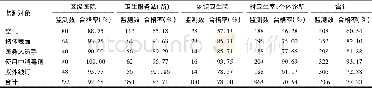
- 表2 濂溪区医疗机构不同对象消毒质量监测情况Table 2 Monitoring of disinfection quality in different items of medical institutions in Lixi dist