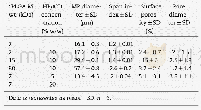
《Table 1–Surface area (SBET) and porosity parameters of Bi2MoO6/ZnInAl-CLDH with different C content
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Three-dimensional biogenic C-doped Bi_2MoO_6/In_2O_3-ZnO Z-scheme heterojunctions derived from a layered precursor》
The specific surface areas and the porous nature of C-doped Bi2MoO6/ZnInAl-CLDH samples were investigated by N2adsorption isotherms as shown in Fig.3a.All four samples with different C contents had type IV isotherms with a distinct hysteresis loop(Sing et al.,1985)due to the microporosity and inter-particle mesoporosity.The Brunner–Emmet–Teller specific surface area of the obtained samples gradually increased from 92.1 to 143.4 m2/g when the C content increased from 0.4 to 1.9 wt.%(Table 1).This phenomenon could be explained by the fact that the Ccontent of the obtained samples mainly derived from the biotemplate,therefore high calcination temperature could cause more carbon vaporization(CO2and CO),and thus led to a drop in the surface area and the collapse of micro-and mesopores.The pore size distribution curves obtained by the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda method(Fig.3b)show that all four samples exhibited multi-peaks in the range of 1–80 nm,indicating that they had hierarchically porous structures containing micro-,meso-and macropores.The hierarchically porous structure could effectively shorten the pathway of mass transfer and facilitate both of adsorption and photocatalysis.
| 图表编号 | XD0052053300 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.05.15 |
| 作者 | Hongyan Li、Jia Li、Ping Yang、Dickon H.L.Ng、Xinling Cui、Fei Ji |
| 绘制单位 | School of Material Science and Engineering, University of Jinan、School of Material Science and Engineering, University of Jinan、School of Material Science and Engineering, University of Jinan、Department of Physics, The Chinese University of Hong Kong、Scho |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |