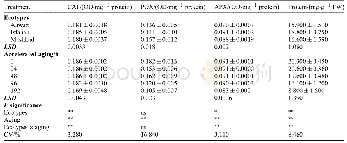
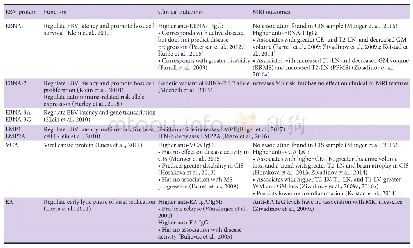
《Table 1 EBV proteins and their effects on MS clinical/MRI outcomes》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《The role of Epstein-Barr virus in multiple sclerosis:from molecular pathophysiology to in vivo imaging》
EBV:Epstein-Barr virus;MS:multiple sclerosis;CIS:clinically isolated syndrome;RRMS:relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis;PPMS:primary progressive multiple sclerosis;EBNA:EBV nuclear antigen;VCA:viral capsid antigen;LMP:latent membrane protein;EA:early an
The initial report of association between infectious mononucleosis occurrence and the subsequent development of MS have been corroborated by multiple meta-analysis(Martyn et al.,1993;Thacker et al.,2006;Handel et al.,2010).Interestingly,the prevalence of both infectious mononucleosis and MS demonstrates a co-localizing and uneven geographical distribution that may be explained by the hygiene hypothesis(Ascherio et al.,2012).According to the hygiene hypothesis,the relative lack of early exposure to common pathogens during childhood in areas of with high levels of sanitation and hygiene may increase the risk for aberrant immune responses and autoimmune diseases if they are exposed to infectious triggers such as EBV later during adolescence and adulthood(Table 1)(Ascherio and Munger,2007) .
| 图表编号 | XD0040609800 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.03.01 |
| 作者 | Yi Guan、Dejan Jakimovski、Murali Ramanathan、Bianca Weinstock-Guttman、Robert Zivadinov |
| 绘制单位 | Buffalo Neuroimaging Analysis Center, Department of Neurology, Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, University at Buffalo,State University of New York、Buffalo Neuroimaging Analysis Center, Department of Neurology, Jacobs School of Medicine a |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1 EBV proteins and their effects on MS clinical/MRI outcomes”的人还看了
-
- Table 3Effect of C.dichotoma extract on fat, TC, and protein intake and faecal excretion of rats fed high-fat diet for f
-

- Tab.2 Effect of different processes on starch gelatinization degree and in vitro protein diges-tibility of conservation
-
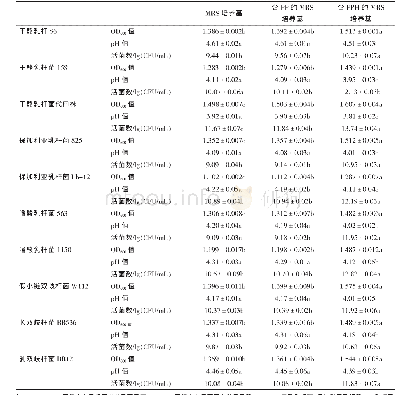
- 表2 豌豆蛋白粉和豌豆蛋白酶解产物对益生菌生长的影响Tabel 2 Effect of pea proteins powder and pea protein hydrolysates on the growth of probiotics
-
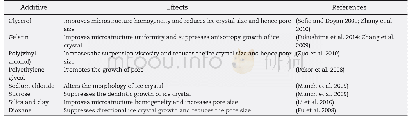
- Table 2–Types of additives used in ice-templating and their respective effects on microstructure evolution.