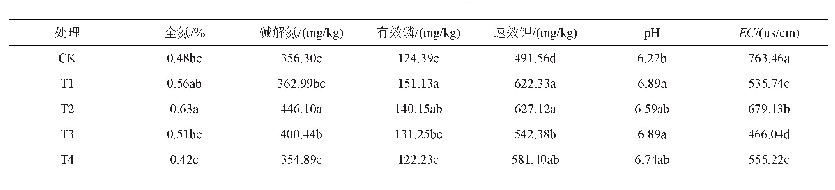
《Table 1–p H, EC (electrical conductivity) , effluent volume and root exudate changes in PBES (plant
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《The plant-enhanced bio-cathode:Root exudates and microbial community for nitrogen removal》
The TOC concentration of the initial influent varied from 395to 415 mg/L.The TOC of the effluent was reduced to less than35 mg/L after 24 hr operation in the PBES,BES and P Control(Fig.3).High TOC removal efficiencies were obtained in the PBES(97%),BES Control(96%)and P Control(96%)(Fig.3) ,which might be attributed to adsorption by the graphite granules and direct uptake by microorganisms and plants in the reactors.The PBES achieved higher TN removal rate(85%)than the BES(72%)and P Control(76%)in this study.These results indicated that the bioelectrochemical process in the PBES played an important role in TOC and TN removal,and the plants in the PMFC may stimulate this process.The hydraulic retention time was set as 24 hr,and the volume of effluent(24 hr)from the PBES(59±6 mL)was less than for the BES Control(85±5 mL)and P Control(76.5±12 mL)(Table 1) .Several factors such as plant absorption,plant transpiration,and evaporation would reduce the water loss in the cathode.The use of plants was not only beneficial for power generation and water purification,but also for reducing the effluent volume by transpiration.Therefore,using plants may reduce subsequent treatment costs for the effluent.
| 图表编号 | XD0033516900 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.03.15 |
| 作者 | Henan Li、Youpeng Qu、Yan Tian、Yujie Feng |
| 绘制单位 | School of Environment, Harbin Institute of Technology、State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment, Harbin Institute of Technology、School of Life Science and Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology、Heilongjiang Academy of Chemical Engin |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |