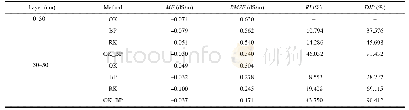
《Table 5 Mapping accuracy test of soil electrical conductivity》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Mapping Soil Electrical Conductivity Using Ordinary Kriging Combined with Back-propagation Network》
Notes:OK,ordinary kriging;BP,back-propagation network;RK,regression kriging;OK_BP,ordinary kriging combined with back-propagation network;ME,mean error;RMSE,root mean squared error;RI,relative improvement;DIP,decrease in the estimation imprecision
The data presented in Table 1 showed that the averages of the soil electrical conductivity for training sites at0–30 cm and 30–50 cm were 1.03 dS/m and 0.55 dS/m,respectively.The soil electrical conductivity decreased with the increase of soil depth,which indicated thatsalts accumulated on the soil surface.According to the classification standard of variability by Nielsen and Bouma(1985),the soil salinity displays strong,medium and weak variability when the coefficient of variations is<10%,10%–100%and>100%,respectively.Accordingly,there were strong and medium spatial variability at the soil depths of 0–30 and 30–50cm,respectively.The soil electrical conductivity for the training sites was positively skewed,while the log-transformed soil electrical conductivity showed approximately normal distribution.Therefore,the mapping of soil electrical conductivity was conducted by log-transformed values,and ultimately,the prediction values of the soil electrical conductivity were back-transformed into the original values using the antilogarithmic function.
| 图表编号 | XD0046962200 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.04.01 |
| 作者 | HUANG Yajie、LI Zhen、YE Huichun、ZHANG Shiwen、ZHUO Zhiqing、XING An、HUANG Yuanfang |
| 绘制单位 | Key Laboratory of Arable Land Conservation (North China), Ministry of Agriculture、Key Laboratory of Agricultural Land Quality Monitoring, Ministry of Land and Resources, College of Resources and Environmental Sciences, China Agricultural University、Key La |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |

![表3 冻土组成物质的导热系数 (W·m-1·K-1) [31]Table 3The thermal conductivities of various frozen soil components (W·m-1·K-1) [31]](http://bookimg.mtoou.info/tubiao/gif/BCDT201801015_40500.gif)


