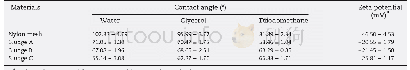
《Table 2–Contact angle and zeta potential of membrane and sludge samples.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Thermodynamic prediction and experimental investigation of short-term dynamic membrane formation in dynamic membrane bioreactors:Effects of sludge properties》
Values of zeta potential were measured in 0.01 mol/L NaCl solution at pH 7.7.
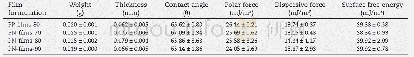
As mentioned,the sludge adhesion behaviors on the membrane were mainly described by the interactions of membrane–sludge flocs.Table 2 lists the contact angles and zeta potentials of the nylon membrane and the three kinds of sludge samples,which are important data for the subsequent XDLVO calculations.Table 3 shows the calculated free energy of adhesion per unit area at contact for each membrane–sludge combination using Eqs.(4)–(6),(8) and(9).Significant differences were recorded for the adhesion free energies in the different membrane–sludge combinations,due to differences in the sludge properties.According to the XDLVO theory,a negative value of interaction energy between the membrane and sludge flocs signified attractive interactions,which facilitates the adhesion of sludge to the membrane.Conversely,a positive value indicated repulsive interaction,which resists adhesion of the sludge to the membrane(Hong et al.,2013).As shown in Table 3,the negative values ofΔGswmTOTin all the membrane–sludge combinations indicated attractive interactions at contact between the nylon membrane and various sludge samples.Moreover,the lowest value ofΔGswmTOTrecorded for the membrane–sludge A combination indicated the strongest level of sludge adhesion on the membrane.On the other hand,compared toΔGd0LWandΔGd0EL,ΔGd0ABcontributed more to theΔGswmTOTfor all the membrane–sludge combinations.Therefore,the AB interaction is demonstrated to play an important role in the sludge adhesion process,which was similar with the results reported previously in the literatures(Brant and Childress,2002;Hong et al.,2013).
| 图表编号 | XD0033516500 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.03.15 |
| 作者 | Zhenzhen Yu、Yisong Hu、Mawuli Dzakpasu、Xiaochang C.Wang |
| 绘制单位 | Key Lab of Northwest Water Resource, Environment and Ecology, MOE, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology、Key Lab of Northwest Water Resource, Environment and Ecology, MOE, Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology、International Science & |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 2–Contact angle and zeta potential of membrane and sludge samples.”的人还看了
-

- Table 1–Effect of different concentrations of propranolol on zeta potential and particle size of the nanoparticles (mean