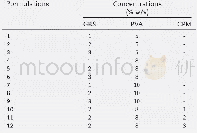
《Table 2Decay parameters of EY in aqueous TEOA solution upon the introduc-tion of Zn-P@g-C3N4, Ni-P@
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《可控设计Zn-Ni-P修饰g-C_3N_4催化剂光催化产氢性能(英文)》
To further investigate the separation and transfer mechanism of the electrons and holes between the excited state eosin and the catalysts and determine the fluorescence lifetimes of Zn-P@g-C3N4,Ni-P@g-C3N4,and Zn-Ni-P@g-C3N4,we used the transient fluorescence spectroscopy technique.Fig.8(b)shows that for all the samples,the fluorescence intensities exponentially decreased,which could be well fitted by using the three radiative lifetimes:[41].The different lifespan changes are shown in Table 2.The longest lifetime increased from 26.34 ns for pure g-C3N4 to 63.68 ns for Zn-Ni-P@g-C3N4,whereas the medium lifetime increased from4.34 ns to 4.94 ns,which showed that the combination of Zn-Ni-P and g-C3N4 effectively increased the lifetime of the charge carriers[42].The result could also explain the good separation efficiency of the photogenerated electron-hole pairs and the effective electron transfer that occurred between Zn-Ni-P and g-C3N4,which was beneficial for improving the photocatalytic H2 production activity.The average life could be calculated by the theoretical formula[43]:
| 图表编号 | XD0028866000 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.03.01 |
| 作者 | 李彦兵、靳治良、张利君、樊凯 |
| 绘制单位 | 北方民族大学化学与化学工程学院、北方民族大学国家民委化工技术基础重点实验室、北方民族大学化学与化学工程学院、北方民族大学国家民委化工技术基础重点实验室、北方民族大学化学与化学工程学院、北方民族大学国家民委化工技术基础重点实验室、北方民族大学化学与化学工程学院、北方民族大学国家民委化工技术基础重点实验室 |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |