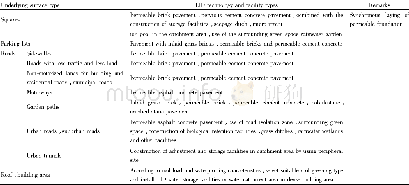
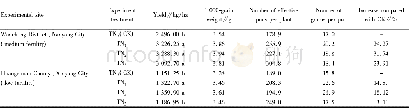
《Table 1–Relevant applications of catalysts in aqueous phase reactions.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Current status of applying microwave-associated catalysis for the degradation of organics in aqueous phase – A review》
The catalysts used to assist microwave reactions can be classified in many ways.For instance,catalysts can be classified as resistance type,dielectric type,and magnetic medium type according to their loss mechanism,or they can be classified as coating type and structural type based on their forming process.Catalysts can also be classified according to their main elemental components,which is the classification method that will be used in this article.Previous studies have concluded that a large proportion of catalysts used in microwave chemical reactions are either carbon-based or iron-based because these elements are abundant in nature and have good absorbing properties(Ania et al.,2007;Augusta and Kalaichelvi,2015;Chang et al.,2010;Chen et al.,2011;Chen et al.,2016a;Chen et al.,2016b;Dalal et al.,2016;Li et al.,2016b;Liao et al.,2010;Liu et al.,2013).However,carbon-based and iron-based catalysts have different absorbing mechanisms;for example,ferrite mainly absorbs microwaves through magnetic loss,while carbon nanotubes mainly absorb microwaves through dielectric loss.The different absorbing mechanisms of these catalysts have determined the field and mode of their applications.Furthermore,there are many catalysts composed of other elements that are not widely used to enhance microwave reactions,such as soft magnetic catalysts,rare earth catalysts,and some special types of catalysts like ionic liquids.These more rarely used catalysts have different absorbing mechanisms;thus,they are often used in special reactions.Table 1 lists relevant applications of catalysts and their effects on aqueous phase reactions exposed to microwave radiation.Different types of catalysts and their applications in microwave reactions are described in the following sections.
| 图表编号 | XD0033529200 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.07.15 |
| 作者 | Chao Xue、Yanpeng Mao、Wenlong Wang、Zhanlong Song、Xiqiang Zhao、Jing Sun、Yanxiang Wang |
| 绘制单位 | School of Energy and Power Engineering, Shandong University、School of Energy and Power Engineering, Shandong University、School of Energy and Power Engineering, Shandong University、School of Energy and Power Engineering, Shandong University、School of Energ |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1–Relevant applications of catalysts in aqueous phase reactions.”的人还看了
-
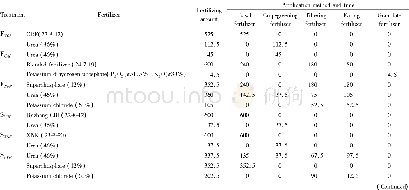
- Table 2 Quantity and application method of fertilizer application in the early and late rice cropping fields and LAD in
-
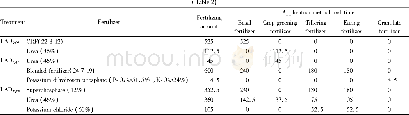
- Table 2 Quantity and application method of fertilizer application in the early and late rice cropping fields and LAD in