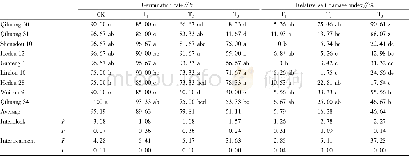
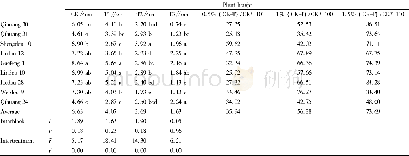
《Table 2 Effect of Na Cl stress on the selectivity SK, Na, SCa, Na of ion absorption and transport o
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Effects of Salt Stress on Growth and Ion Distribution in Seedlings of Asparagus officinalis L.》
a,b,c indicate significant differences at the level of P<0.05.
In terms of plant morphology,when Na Cl≤100 mmol/L,the A.officinalis seedlings showed no obvious salty damage symptoms.When the Na Cl concentration increased to 200 mmol/L,the leaves at the top of seedlings showed the symptoms of chlorosis and yellowing,and when Na Cl increased to 300 mmol/L,the leaves at the top of the seedlings were withered.As shown in Table 1,the fresh weights of the roots(r=-0.988,P<0.01)and aerial parts(r=-0.985,P<0.01)of A.officinalis seedlings were negatively correlated with Na Cl concentration under Na Cl stress,and the difference reached the significant level with the control at Na Cl≥100 mmol/L(P<0.05).There was no significant difference from the control in plant heights,root dry weight and aerial part dry weight at Na Cl≤100 mmol/L,but with the increase of salt concentration,plant heights,dry weight of roots and dry weights of the aerial parts gradually decreased and showed significant difference with the control(P<0.05).The water content in the root and aerial part decreased with the increase of salt stress.The water content of the aerial parts showed significant difference from the control at Na Cl≥200 mmol/L(P<0.05),but the water content in roots did not reach a significant level in each treatment.
| 图表编号 | XD00183065300 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.08.01 |
| 作者 | Yanpo CAO、Peng DAI、Suying DAI |
| 绘制单位 | Institute of Cash Crops,Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences、Institute of Cash Crops,Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences、Institute of Cash Crops,Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 2 Effect of Na Cl stress on the selectivity SK, Na, SCa, Na of ion absorption and transport of A.officinalis seedl”的人还看了
-

- Table 4–The effect of selected CS molecular weight and concentration on surface porosity%for plain PLGA MPs using double
-
- Table 5 Effect of Na Cl stress on fibrous root growth of soybean cultivars bred in Shandong Province