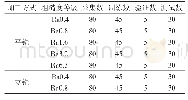
《表1 使用PMMA/氧化铈复合颗粒精加工后硅片的表面粗糙度》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《抛光压力和抛光垫硬度对PMMA-CeO_2核壳复合磨粒抛光性能的影响(英文)》
The polishing pads used in CMP processes are another key factor that influences the final surface roughness[27].And the elastic modulus and surface hardness are important mechanical properties for the polishing pads.In our experiments,the HSA of the used MD-Chem pad and IC-1000 pad were determined to be about 74±2 and 96±1,respectively.Table 1 provides the Ra and RMS roughness data of the surfaces after CMP using PMMA-ceria particles with different polishing pads and polishing pressures(p).For a given pressure of 3 psi(Fig.7),the soft MD-Chem pad results in relatively low surface roughness(Rais (0.18±0.03)nm,RMS roughness is(0.23±0.02)nm) with respect to the hard IC-1000 pad(Rais (0.29±0.02)nm,RMS roughness is(0.36±0.02)nm) .Moreover,the sectional profile analyses also reveal that the soft MD-Chem pad achieves in a topographical variation of±0.3 nm,which is also lower than that of the hard IC-1000pad(±0.6 nm) .In order to explore the mechanisms of the material removal in the free abrasive polishing process,a theoretical model was proposed by Bhushan and coworkers[28]to predict the relationship among the polishing parameters(particle diameter,polishing pad and nominal contact pressure),the wear rate and the surface roughness.It is revealed that the surface roughness increases with the increases of the particle diameter and pad hardness.Moreover,T.Eusner et al[29]further confirmed that a reduced maximum value of the local pad hardness resulted in a decreased upper limit for the normalized indentation width and depth.Therefore,the applications of soft pads with small hardness variation and nano-sized abrasive particles contributed to the scratch elimination and the achievement of precise non-defective surfaces.The presented polishing results in this work are in accord with the theoretical predictions mentioned above.Furthermore,the same tendency can also be found in the case of polishing pressure of 6 psi(Fig.9).The soft pad also results in lower roughness(Rais (0.31±0.02)nm,RMS roughness is(0.38±0.03)nm) and lower topographical variation(±0.5 nm) than those achieved by the hard pad(Rais (0.40±0.06)nm,RMS roughness is(0.51±0.06)nm,and topographical varitation is±0.7 nm,respectively) .As proposed by F.G.Shi et al[30],an increased polishing pressure applied to the substrate did not markedly increase the local force applied to each particle and the indentation depth of an abrasive particle.Based on the contact mechanics mechanism,a decreased indentation depth commonly results in a reduced surface roughness.Therefore,the surface roughness does not increase significantly with an increased polishing pressure.
| 图表编号 | XD0083677900 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.10.15 |
| 作者 | 马翔宇、陈杨 |
| 绘制单位 | 常州大学材料科学与工程学院、常州大学材料科学与工程学院 |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
![表3 不同掺杂区域的硅片表面的复合速率的参数[2]](http://bookimg.mtoou.info/tubiao/gif/TYNZ202010001_05000.gif)