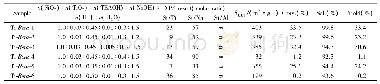
《Table 1Physicochemical properties of catalysts.》
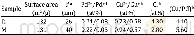 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Pd-Cu-Cl_x/Al_2O_3催化剂对CO氧化的稳定性(英文)》
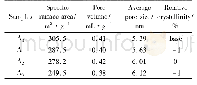
a Crystallite size of Cu2(OH)3Cl as obtained from XRD(Fig.3)b Obtained from XPS.
The H2-TPR profiles and H2 consumption of catalysts are shown in Fig.4.and Table 2,respectively.Pd/Al2O3 had an obvious H2 reduction peak at 38°C,while Cu/Al2O3 revealed twosuch peaks at 239 and 311°C.With the introduction of Cu to Pd/Al2O3,two distinct reduction peaks at 100–250°C and250–400°C were observed.Compared with the single metal catalysts,it was known that the presence of Pd promoted the reduction of Cu species.The intense reduction peak with a shoulder in the temperature range 100–250°C can be de-convoluted into two reduction peaks:one(peak A)was ascribed to the reduction of Pd species and the other(peak B)to the reduction of copper species,which was in close contact with the Pd species.The high-temperature reduction peak(peak C)at 250–400°C was attributed to the reduction of isolated copper species[23,24].
| 图表编号 | XD008196900 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.09.01 |
| 作者 | 王丽、路小清、王维、詹望成、郭杨龙、郭耘 |
| 绘制单位 | 华东理工大学大学化学与分子工程学院工业催化研究所、华东理工大学大学化学与分子工程学院工业催化研究所、华东理工大学大学化学与分子工程学院工业催化研究所、华东理工大学大学化学与分子工程学院工业催化研究所、华东理工大学大学化学与分子工程学院工业催化研究所、华东理工大学大学化学与分子工程学院工业催化研究所 |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |