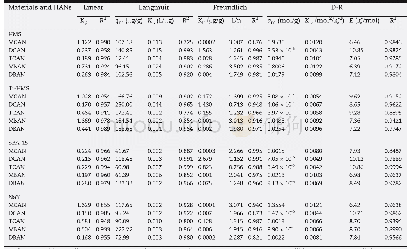
《Table 4–Isotherm parameters derived from the Linear, Langmuir, Freundlich, and Dubinin and Radushke
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Adsorption of single and mixed haloacetonitriles on silica-based porous materials: Mechanisms and effects of porous structures》
Kp:linear partition coefficient;qm:maximum adsorption capacity;KL:Langmuir constant;KF:Freundlich constant;n:Freundlich constant related to adsorption intensity;KD:the constant related to adsorption energy;E:mean free energy of adsorption.
The derived Linear,Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm parameters are listed in Table 4.Since the equilibrium concentration was low,the Linear isotherm fits well to the experimental results with a high R2(>0.91),except for the case of MCAN adsorption on NaY(R2=0.855).A high Kpvalue indicates a high affinity of adsorbent for HAN adsorption.For the adsorption of HANs onto the Ti-HMS and NaY adsorbents,the data best fits the Freundlich model,as evidenced from the R2values,which supports the heterogeneous distribution of the silanol groups and the Lewis acid sites in the titanium substitution of Ti-HMS,and the Na+and silanol groups on the NaY surface.On the other hand,the adsorption equilibrium of HANs on SBA-15 was likely to be described by both models implying a multilayer coverage may occur on homogeneous surface of silanol group uniformity on SBA-15 surface However,the HAN adsorption data distribution on HMS fitted well with the Freundlich model rather than the Langmuir one despite the fact that the surface of HMS has a relatively uniform silanol group distribution.Note,however,that the evaluation of the adsorption at high HAN concentrations is required for confirmation.
| 图表编号 | XD0052064100 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.05.15 |
| 作者 | Panida Prarat、Chawalit Ngamcharussrivichai、Sutha Khaodhiar、Patiparn Punyapalakul |
| 绘制单位 | International Postgraduate Programs in Hazardous Substance and Environmental Management, Graduate School, Chulalongkorn University、Center of Excellence on Hazardous Substance Management (HSM), Chulalongkorn University、Department of Chemical Technology, Fa |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |