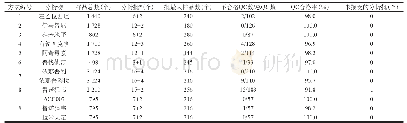
《Table 1 Characteristics of the analytical methods for hemoglobin A1c measurement》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Update on biomarkers of glycemic control》
DCCT:Diabetes Control and Complications Trial;HbF:Fetal hemoglobin;GHb:Total glycated hemoglobin.
Various analytical methods for HbA1c determination commonly utilize either of the two principles(Table 1):(1)HbA1c separation from other hemoglobin fractions that is based on charge differences using either chromatography or electrophoresis;or(2)the direct measurement of HbA1c by specific binding(immunochemistry or affinity)or enzymatic cleavage[22].Due to differences between these analytical methods in their use of different principles and a lack of standardization,HbA1c testing inherently suffers from a significant between-method variability which has seriously affected its clinical accuracy in the longitudinal monitoring of average glycemia with different methods and comparing the results of the DCCT-and UKPDS-derived targets.Heterogeneity of molecular entities that were measured by different methods significantly contributed to the analytical variability,as the glycation reaction involved not onlyβ-N-terminal valine but also other accessible amino groups within theαandβ-globin chains,and these results depended on the type of analyte that was captured by a particular method[12].Thus,the standardization of the HbA1c measurement and reporting that included a uniform definition of the analyte was shortly identified as one of the most important issues in diabetes care[23,24].
| 图表编号 | XD0043270700 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.15 |
| 作者 | Maja Krha、Marijana Vui Lovreni |
| 绘制单位 | Division of Laboratory Medicine, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine, Merkur University Hospital、Division of Laboratory Medicine, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine, Merkur University Hospital |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |