《Table 3 Characteristics of glycaemic biomarkers》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Update on biomarkers of glycemic control》
HbA1c:Hemoglobin A1c;SMBG:Self-monitoring of blood glucose;CGMS:Continuous glucose monitoring system.
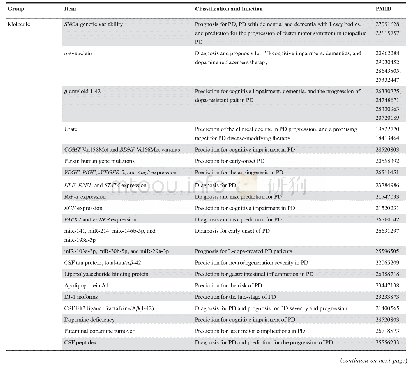
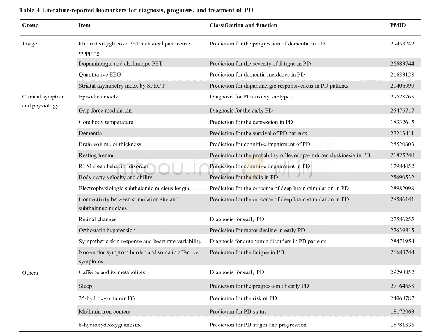
Hyperglycemia is a key biochemical feature of diabetes that should be rigorously controlled and maintained in a range as close to normal as possible to mitigate the risk of diabetic complications.Both the level of and exposure to hyperglycemia,as well as glycemic variability,contribute to the pathogenesis of diabetic complications,with different patterns of disease pathogenesis in patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.Despite its analytical and biological limitations,HbA1c remains the key biomarker of long-term glycemic control.However,it has become apparent in recent years that other glycated proteins,1,5-AG,and integrated measures from direct glucose testing by SMBG/CGMS may provide valuable data complementary to HbA1c,particularly in circumstances when the HbA1c results may be unreliable or insufficient to assess the risk of adverse outcomes(Table 3).Long-term associations of these alternative biomarkers of glycemia with the risk of diabetic complications need to be investigated to provide clinically relevant cut-off values and validate their utility in diverse populations of patients with diabetes.
| 图表编号 | XD0043270600 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.15 |
| 作者 | Maja Krha、Marijana Vui Lovreni |
| 绘制单位 | Division of Laboratory Medicine, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine, Merkur University Hospital、Division of Laboratory Medicine, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine, Merkur University Hospital |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |