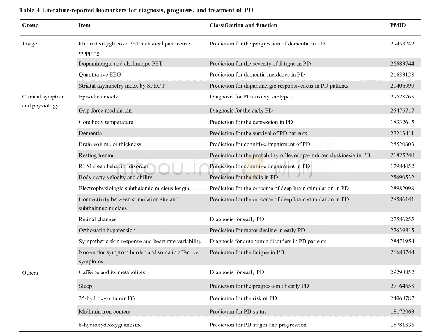
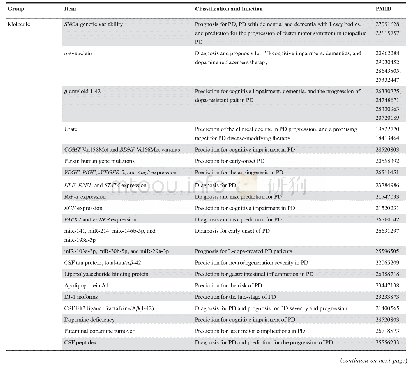
《Table 4 Literature-reported biomarkers for diagnosis,prognosis,and treatment of PD》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Translational Informatics for Parkinson's Disease:from Big Biomedical Data to Small Actionable Alterations》
Note:Molecule types includes gene,RNA,protein,and metabolite;CSF,cerebrospinal fluid;PET,positron emission tomography;EEG,electroencephalograph;SPECT,single photon emission computed tomography;REM,rapid eye movement.
As illustrated in Table 4,biological molecules,such as genes,RNAs,proteins,and metabolites,play important roles in PD evolution.For example,cerebro-spinal fluid(CSF)asynuclein was one of the well-studied proteins implicated in PD pathogenesis,and its genetic variability was a prognostic marker for PD,PD with dementia,and dementia with Lewy bodies[32].Ritz et al.[33]demonstrated that a-synuclein genetic variants were associated with the development of faster motor symptoms in idiopathic PD.In addition,Ballard et al.[34]reported that CSF a-synuclein had the potential for diagnosing PD and related dementias.Mollenhauer et al.[26]found that CSF a-synuclein was also a useful indicator in PD patients undergoing dopamine replacement therapy.Moreover,plasma and skin nerve a-synuclein is valuable in predicting PD cognitive impairment and idiopathic PD,respectively[35,36].Another key player,CSF b-amyloid 1–42,was a powerful predictor of the progression of cognitive impairment,dementia,and dopa-resistant gait in PD.For example,a lower level of CSF b-amyloid 1–42 was common in advanced PD patients with cognitive decline and could be used to predict cognitive impairment in newly diagnosed PD[37].Alves et al.[38]indicated that the CSF levels of bamyloid 1–42 were lower in PD patients with dementia.The abnormal expression of this protein increased the risk of dementia development,which was used for the early prognosis of PD dementia[38].Moreover,a decrease in b-amyloid 1–42was also involved in the pathology of dopa-resistant gait in early PD[39].
| 图表编号 | XD00117311400 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.08.01 |
| 作者 | Bairong Shen、Yuxin Lin、Cheng Bi、Shengrong Zhou、Zhongchen Bai、Guangmin Zheng、Jing Zhou |
| 绘制单位 | Institutes for Systems Genetics, West China Hospital, Sichuan University、Center for Systems Biology, Soochow University、Center for Systems Biology, Soochow University、Center for Systems Biology, Soochow University、Center for Translational Biomedical Infor |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 4 Literature-reported biomarkers for diagnosis,prognosis,and treatment of PD”的人还看了
-

- Table 4.Performance assessment of related hematological parameters for diagnosis ofα-thalassemia in females