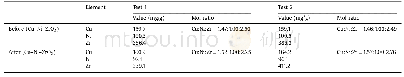
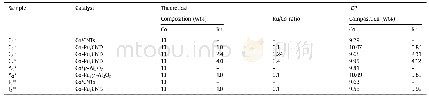
《Table 5.H2-TPD data and O2titration of the Co-based catalysts.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Fischer–Tropsch synthesis using Co and Co-Ru bifunctional nanocatalyst supported on carbon nanotube prepared via chemical reduction method》
As was mentioned in earlier studies[51–55],the reaction conditions such as temperature,pressure,H2/CO ratio and GHSV have presented the significant influential factors on the catalyst activity and product distribution in a FTS.In the present work,the reaction conditions were chosen as H2/CO=2,P=20 bar,T=220–240°C,and GHSV=1400 h-1based on the previous experiments[7,8,21,28].Using all of the Co-and Co(Ru)-based catalysts,the FTS was carried out at the different reaction conditions and the results of carbon monoxide conversion and product distributions are shown in Table 6.As shown in this table,under the same process conditions,the C2–C4catalysts presented higher selectivity toward C5+and the lower CH4selectivity than C1catalyst.Similarly,the I2and A2catalysts demonstrated a similar behavior in comparison with I1and A1.Ru compared to Co presented higher tendency for production of the C5+,however this tendency could be enhanced by presence of both Ru and Co indicating the synergism effect between these two metals[7,18,52].Hence,the enhancement in C5+selectivity for all the Ru/Co-based catalysts(C2–C4,I2and A2)as compared to Co-based catalysts(C1,I1and A1)could be attributed to the presence of ruthenium beside the Co.On the other hand,in the case of catalysts prepared using chemical reduction method,the results could be ascribed to the formation of the larger cobalt particles at C2–C4and A2catalysts compared to C1and A1,respectively.In the various studies[10,21,29,42,54],it has been concluded that the larger cobalt cluster show higher tendency for C5+production,while the small cluster size was more favored for higher selectivity towards CH4.As shown in Table 6,the catalysts synthesized by substitution reaction technique(C1 (43.68%)and C2(68.83%)) gave the higher C5+selectivity than those prepared by impregnation route(I1 (41.69%)and I2(59.30%)) .Apparently,the uniformity of the particle size in the case of the catalysts prepared by reduction method led to the improvement of the hydrogenation of CO,which in turn enhanced the C5+selectivity[48].Moreover,pursuant to Table 6,the C5+selectivity and CH4selectivity were(43.68%and 27.98%)for C1,and(37.69%and 34.35%)for A1at 220°C,respectively.In another word,the CNT support led to higher heavy hydrocarbon production and lower methane selectivity thanγ-Al2O3support.Although the CNT supported catalyst presented smaller cobalt clusters,however the enhancement in C5+selectivity and reduction in CH4selectivity could be attributed to the use of the chemical reduction technique in preparation of the Co/functionalized CNT that led to particle’s confinement inside the nanotubes.Karimi et al.[47]prepared a type of Co/functionalized CNTs catalyst using micro emulsion procedure so that through FTS their results were compared with those obtained using Co/common CNTs catalyst.They concluded that the FTS rate and CO conversion changed from 0.64 to 0.78 and 44.8%to 56.8%,respectively,for the treated and untreated CNT.In addition,in their work C5+selectivity increased about 7.4%and CH4selectivity decreased about 44%,through functionalization of CNT.Thus,it should be noted that crystallite’s confinement inside the nanotubes could be more effective in comparison with size distribution of cobalt clusters[3,47,55,56].Hence,one may concluded that the particle’s confinement inside CNTs might be a key parameter for the FTS performance compared to the crystallite size[55].On the other hand as shown in Table 6,increasing the amount of Ru from 1%to 2.4%,led to reduction of the CH4selectivity from15.08%to 11.81%and from 15.26%to 12.60%at 220 and 240°C,respectively.In another word,the selectivity of higher molecular weight hydrocarbons enhanced about 7%for low Ru loading,however,by enhancing Ru content from 2.4%to 4%,the CH4and C5+selectivity changes were little that could be attributed to more surface diminution of Ru atoms[7,18,42].
| 图表编号 | XD0042894100 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.01 |
| 作者 | Jafar Shariati、Ali Haghtalab、Amir Mosayebi |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Chemical Engineering, Tarbiat Modares University、Department of Chemical Engineering, Tarbiat Modares University、Department of Chemical Engineering, Tafresh University |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |