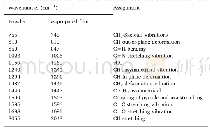
《Table 1–Most probable number (MPN) enumerations of Fe (III) -reducing and nitrate-dependent Fe (II)
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Effects of O_3/Cl_2 disinfection on corrosion and opportunistic pathogens growth in drinking water distribution systems》
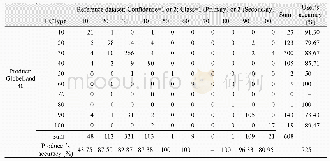
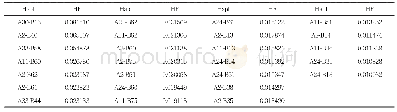
The chemical parameters of water quality were the main factors which influenced the corrosion process in DWDSs(Yang et al.,2012).The main chemical parameters,including Cl-,SO42-,alkalinity,dissolved oxygen(DO)and p H,were measured in the influents of both ARs(Appendix A Table S4).There was no significant difference in water quality between the influents of both ARs(p>0.05).However,the microbiologically influenced corrosion(MIC)also played a great role in stable corrosion scales formation(Sun et al.,2014;Wang et al.,2014;Jin et al.,2015).The iron-oxidizing bacteria(IOB)and ironreducing bacteria(IRB)can influence the corrosion process and the composition of the corrosion scales.Therefore,the potential corrosive bacteria including IOB and IRB were identified using the most probable number(MPN)technique(Coby et al.,2011).The results showed that the abundance of IOB and IRB in the biofilms of corrosion scales in AR treated with O3/Cl2disinfection was 1.2×109and 4.5×107cells/g corrosion scales,respectively,which was higher than that in the biofilms of AR treated with Cl2alone(Table 1).
| 图表编号 | XD0025355100 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.11.15 |
| 作者 | Haibo Wang、Chun Hu、Suona Zhang、Lizhong Liu、Xueci Xing |
| 绘制单位 | Key Laboratory of Drinking Water Science and Technology,Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences,Chinese Academy of Sciences、Key Laboratory of Drinking Water Science and Technology,Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences,Chinese Academy of Sc |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |