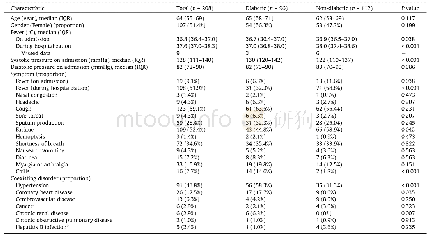
《Table 1 Clinical characteristics of patients with RAO associated with trauma》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Central retinal artery occlusion and traumatic optic neuropathy following blunt ocular trauma》
RAO:Retinal Artery Occlusion;VA:Visual acuity;NLP:No light perception;CRAO:Central retinal artery occlusion;CRVO:Central retinal vein occlusion;N/A:Not available;TON:Traumatic optic neuropathy;ONA:Optic nerve avulsion;CT:Computed tomography;FA:Fluorescein
A summary of all 17 cases of trauma associated CRAO in healthy patients found in literature is presented in Table 1.RAO associated with trauma occurred in both genders and in patients aged between 6 and 47y,in both eyes,after mild sports related trauma or after more serious trauma such as during a road traffic accident.Most of these cases presented with sudden painless visual loss which occurred either immediately or a few hours after the trauma.However,late onset CRAO was noted in one case which occurred 6mo after the trauma with a ball[8].In most cases,anterior segment appeared to be normal with positive relative afferent pupillary defect(RAPD).This may be accompanied with conjunctival hyperaemia or haemorrhage,hyphema,or severely swollen eyelids in cases of orbital blow out fractures.Associated findings include periocular bruising,mandibular and orbital fractures and loss of consciousness.Posterior segment findings included an oedematous and pale retina,arteriolar attenuation and cherry red spot(noted in 70%of cases:12 out of 17 cases).This assessment also presents 3 cases of simultaneous CRAO and CRVO where flame shaped and pre-retinal hemorrhage were noted as well[7,18,22].FA showed either delayed retinal filling and arterial narrowing or obstruction with normal choroidal filling.In cases of macular infarction,FA also demonstrated areas of hypofluorescence at the macula,while additional staining of the ON head is noted in cases of associated TON[11,20].
| 图表编号 | XD0023063100 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.05.18 |
| 作者 | Jasmin Zvornianin、Ferenc Kuhn、Meliha Halilbai、Zlatko Muanovi |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Ophthalmology,University Clinical Center Tuzla、International Society of Ocular Trama Birmingham、Milos Eye Clinic、Zagorskiego Eye Clinic、Department of Ophthalmology,University Clinical Center Tuzla、Department of Ophthalmology,University Clini |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |