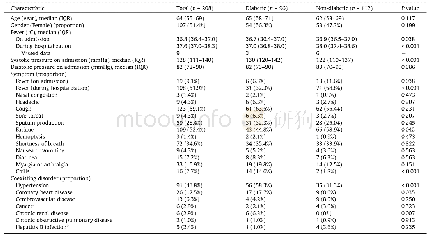
《Table 1 Clinical characteristics of 43 patients with gastric neuroendocrine carcinomas》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Clinical significance of programmed death 1/programmed death ligand 1 pathway in gastric neuroendocrine carcinomas》
Patients were staged in accordance with the 7th Edition of the AJCC Cancer TNM Classification.OS:Overall survival.
For Kaplan-Meier analysis,the OS of patients with high expression of PD-L1 was significantly shorter compared with patients with low PD-L1 expression(P=0.016).We also found that patients with high CD8+T cell infiltration may have a better clinical prognosis,however,due to the limited patient cohort,the P-value did not reach the statistical significance(P=0.065).Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to assess the impact of potential prognostic factors on OS.As shown in Table 3,corpus tumor[hazard ratio(HR)=3.034,P=0.032],liver metastasis(HR=3.515,P=0.016),and PD-L1 expression(HR=2.846,P=0.021)were significantly associated with OS in univariate analysis,while multivariate analysis demonstrated that only liver metastasis(HR=4.045,P=0.031)and PD-L1 expression(HR=3.646,P=0.009)were independent prognostic factors.Based on the theory that PD-L1 played a role in immune evasion by suppressing the function of PD-1 positive immune cells,we divided the patients into two groups depending on the infiltration of PD-1positive cells and performed the Kaplan-Meier analysis to explore the influence of PD-L1 expression on patients’survival.The results suggested that in the low PD-1+cell infiltration group,patients’survival was not associated with PD-L1 expression statistically(Figure 3C,P=0.242);while in the high PD-1+cells infiltration group,patients with high expression of PD-L1 had a significantly shorter survival(Figure3D,P=0.013).
| 图表编号 | XD0064278000 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.04.14 |
| 作者 | Min-Wei Yang、Xue-Liang Fu、Yong-Sheng Jiang、Xiao-Jing Chen、Ling-Ye Tao、Jian-Yu Yang、Yan-Miao Huo、Wei Liu、Jun-Feng Zhang、Pei-Feng Liu、Qiang Liu、Rong Hua、Zhi-Gang Zhang、Yong-Wei Sun、De-Jun Liu |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University、Department of Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University、Department of Biliary-Pancreatic Surg |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1 Clinical characteristics of 43 patients with gastric neuroendocrine carcinomas”的人还看了
-
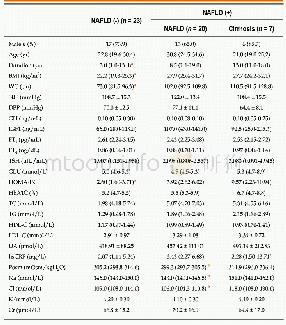
- Table 1 Clinical characteristics of hypopituitary patients with or without non-alcoholic fatty liver disease