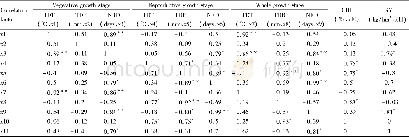
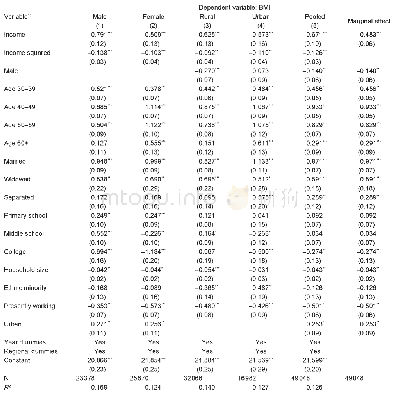
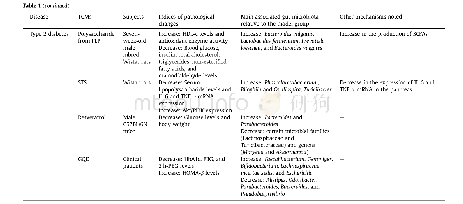
《Table 1Researches on the relationship between H.pylori and PHG.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Helicobacter pylori and portal hypertensive gastropathy》
Until now,most of the literatures attempted to illuminate the role of H.pylori in the development of PHG,but the effects of PHG on H.pylori colonization,proliferation and its virulence to gastric mucosa,even the translocation of itself and its products were rarely studied(Table 1).Some studies[5–7]found that the H.pylori infection rate was lower in cirrhotic patients than that in normal people.These studies also found a positive correlation between PHG and intestinal metaplasia.According to these studies,we infer that the decline of H.pylori infection prevalence in patients with cirrhosis may be related to the intestinal metaplasia of gastric mucosa.H.pylori was unlikely to contribute to the pathogenesis of congestive gastropathy[8]and the eradication of H.pylori in cirrhotic patients seems unnecessary[9–11].Bhargava et al.[12]concluded that H.pylori was inhospitable in PHG and H.pylori had no influences on PHG.Abbas et al.[13]found the existence of H.pylori had no effects on severity of PHG and H.pylori with CagA and CagE was decreased in moderate to severe PHG.Kim et al.[14]found that H.pylori infection rate was significantly lower in cirrhotic patients compared with non-ulcer dyspepsia,and peptic ulcer without chronic liver disease patients.They also found H.pylori prevalence was higher in virus related cirrhosis compared with alcoholic cirrhosis and it was decreased with the increase of Child-Pugh grade.It is interesting that the infection rate of H.pylori had no difference in cirrhosis with or without peptic ulcer,which is exactly opposite to a previous prospective study[15].
| 图表编号 | XD0020459600 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.12.15 |
| 作者 | Ji-Ke Hu、Xue-Mei Li、Bao-Hong Gu、Fan Zhang、Yu-Min Li、Hao Chen |
| 绘制单位 | The Second Clinical Medical College of Lanzhou University、The Second Clinical Medical College of Lanzhou University、The Second Clinical Medical College of Lanzhou University、The Second Clinical Medical College of Lanzhou University、The Key Laboratory of t |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1Researches on the relationship between H.pylori and PHG.”的人还看了
-
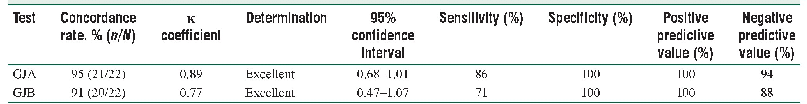
- Table 1:Concordance rates and accuracy between H.pylori antigen test results from fecal samples and those from gastric j
-

- Table 7 Robustness test of the relationship between customer concentra-tion and agricultural enterprise value