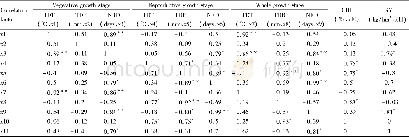
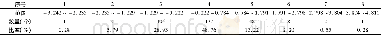《Table 5 The relationships between ecological conditions and grain yield》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Yields and Nitrogen Use Efficiencies of Rice (Oryza sativa) at Different Sites Using Different Nitrogen Fertilizer Application Rates and Controlled-release Urea to Conventional Urea Ratios》
TDT(x1),TDR(x2)and NRD(x3)represent total daily temperature,total daily rainfall,and no rain days of the vegetative growth stages,respectively;TDT(x4),TDR(x5)and NRD(x6)represent total daily temperature,total daily rainfall,and no rain d
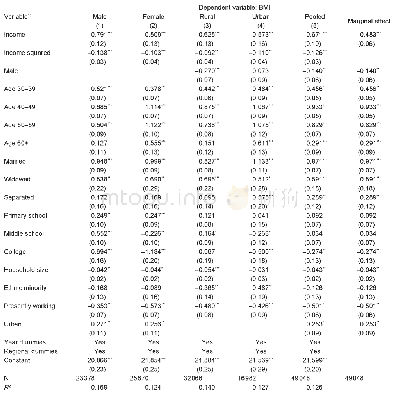
The yields at the two fertilization levels and the CRU∶U ratio were significantly correlated(R=0.810 0,P<0.05;Fig.2).As shown in Fig.2,adding fertilizer had a stronger yield-increasing effect when the soil fertility was lower and a higher CRU∶U ratio gave a stronger yield-increasing effect.These findings indicated that the paddy fields had low nutrient-retention capacities.Large amounts of nutrients were lost after U was applied,but CRU better addressed nutrient deficiencies in the test paddy fields throughout the rice growth period.The cumulative daily mean temperature in the vegetative growth stage was positively correlated with rice yield(Table 5).This correlation was not significant,but the daily mean temperature in the vegetative growth stage would have affected rice growth and nutrient uptake.Excessive application of chemical fertilizers in recent decades has damaged the structures of paddy fields.The water-and nutrient-retention capacities of paddy fields have decreased,and environmental pollution and rice production costs have increased.It is important to change the types of nitrogen fertilizer used to produce rice,that is,to switch to controlled-release fertilizers to decrease nitrogen losses and improve nitrogen use efficiency.This will decrease nitrogen application rate,rice production cost,and environmental pollution.
| 图表编号 | XD00183042900 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.06.01 |
| 作者 | Hong XIONG、Lin ZHANG、Yongchuan ZHU、Xiaoyi GUO、Peng JIANG、Mao LIU、Xingbin ZHOU、Fuxian XU |
| 绘制单位 | Rice and Sorghum Institute,Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences、Key Laboratory of Southwest Rice Biology and Genetics and Breeding,Ministry of Agriculture、Luzhou Branch of National Rice Improvement Center、Rice and Sorghum Institute,Sichuan Academy of |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 5 The relationships between ecological conditions and grain yield”的人还看了
-
- 表5 安徽传统村落空间分布与平面曲率关系Table 5 The relationship between spatial distribution and plan curvature of Anhui traditional villag
-
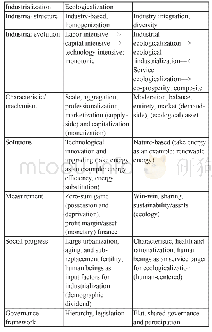
- Table 2:Comparison of the Connotations and Characteristics between Industrialization and Ecologicalization