《Table 4 Trends in seasonal average air temperature for three geographic zones in China》
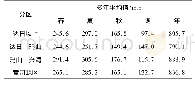
Beyond the seasonal differences during the warming hiatus across China,there are differences across the three geographic zones.Table 4 shows the trends in air temperature for three geographic zones across different seasons and periods.Slowed warming in the eastern monsoon region is mainly reflected in changes in winter air temperature,whose trends were–0.896℃/10a in winter and 0.134℃/10a in summer for 1998–2012.In the northwestern arid region,the trend magnitudes were–1.425℃/10a in winter and 0.217℃/10a in summer for1998–2012.The air temperatures in spring and autumn showed insignificant cooling trends.In high frigid region of the Tibetan Plateau,the warming rate was 0.337℃/10a in summer during 1998–2012,lower in spring and winter,and autumn showed a slight cooling trend.In summary,winter contributed the most to the warming hiatus and summer had the smallest contribution in eastern and northwestern China.In addition,temperature increases were the fastest in summer on the Tibetan Plateau.
| 图表编号 | XD0062091900 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.04.01 |
| 作者 | 杜勤勤、张明军、王圣杰、车存伟、马荣、马转转 |
| 绘制单位 | College of Geography and Environmental Science,Northwest Normal University、College of Geography and Environmental Science,Northwest Normal University、College of Geography and Environmental Science,Northwest Normal University、College of Geography and Envir |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 4 Trends in seasonal average air temperature for three geographic zones in China”的人还看了
-
- 表2 黄河源区多年平均年、季节蒸发量Table 2 The annual and seasonal average pan evaporations in the source regions of the Yellow River
-

- Table 5 Ten-day average temperature and average precipitation in each growth stage of spring maize in Pengzhou City in t
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式





