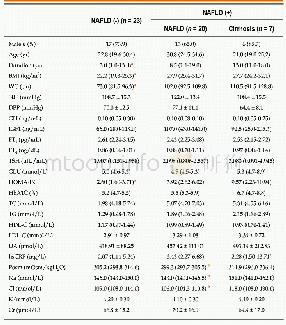
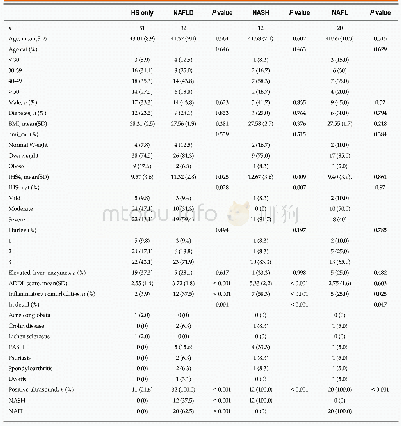
《Table 4 Dysbiosis in human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《"Current status, problems, and perspectives of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease research"》
NAFLD:Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease;NASH:Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Evaluation of liver fibrosis:Considering recent trends,the need for less invasive,more accurate methods of assessing liver fibrosis has produced several potential fibrosis indicators.Platelet count and serum levels of hyaluronic acid,type 4 collagen7S,Mac2-binding protein,and autotaxin are promising biomarkers that predict advanced fibrosis(Table 1)[58-63].Although those single indicators are simple,convenient,and useful for busy clinicians,it should be emphasized that results may be influenced by underlying conditions,such as co-existing collagen disease,systemic inflammation,and renal dysfunction.NAFLD fibrosis score,AST-to-platelet ratio index(APRI),FIB-4 index,BARD,CA index,ELF,and FibroTest have also been proposed as indices to predict advanced fibrosis in NAFLD patients(Table 2)[64-71].ELF and FibroTest use direct markers of collagen synthesis and degradation,but such measurements are uncommon in clinical situations.In contrast,NAFLD fibrosis score,APRI,and FIB-4 exploit the biochemical test components of age,AST,ALT,glucose,BMI,platelets and albumin,all of which are routinely obtained in clinical practice.However,the scores of these indices tend to be increased in the elderly,and it is also unclear whether changes in AST,ALT,and BMI are correlated with the degree of actual fibrosis.For more global applicability,the cut-off values of single biomarkers and panels will require optimization according to country,race,sex,age,and other factors.
| 图表编号 | XD0049331400 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.14 |
| 作者 | Naoki Tanaka、Takefumi Kimura、Naoyuki Fujimori、Tadanobu Nagaya、Michiharu Komatsu、Eiji Tanaka |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Metabolic Regulation, Shinshu University School of Medicine、International Research Center for Agricultural Food Industry, Shinshu University、Department of Internal Medicine, Shinshu University School of Medicine、Department of Internal Medici |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 4 Dysbiosis in human non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis”的人还看了
-

- Table 1 Gut microbiota associated changes in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis subject
-
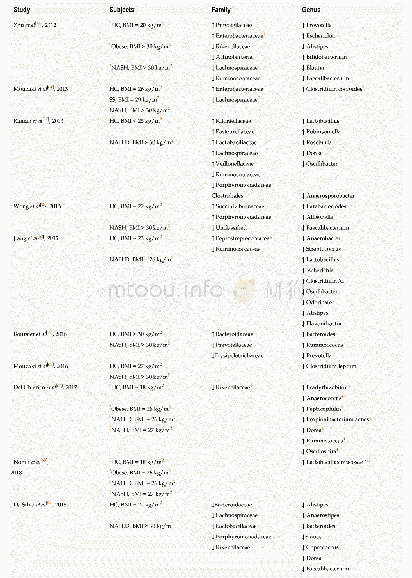
- Table 1 Gut microbiota associated changes in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis subject