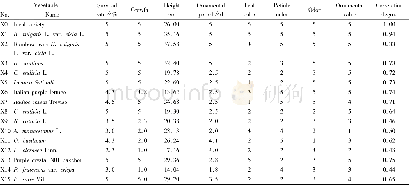
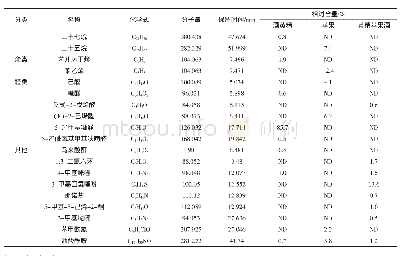
《Table 4 Sources of flavonoid compounds and their antifungal activities》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Role of flavonoids in plant interactions with the environment and against human pathogens-A review》
Flavonoids can be classified according to biosynthetic origin.Some classes,for example chalcones,flavanones,flavan-3-ols and flavan-3,4-diols,are both intermediates in biosynthesis as well as end products that can accumulate in plant tissues(Cushnie and Lamb 2005).While,some intermediates are only produced as the end product of the biosynthesis pathway such as flavonols,flavones,and proanthocyanidins(Sannomiya et al.2005).Plants may contain about 700 isoflavones and 3 000 flavones(de Rijke et al.2006).Table 1 illustrates the classes of flavonoids and their representative compounds.Based on the molecular structure,flavonoids can be divided into 8 groups such as flavanone,flavones,flavonols,isoflavones,catechin,anthocyanidins,chalcone and dihydro flavanols(Tsuchiya2010).They can also be classified into 6 groups based on the heterocyclic ring variation including isoflavones,anthocyanidins,catechins,flavanones,flavonols and flavones(Hollman and Katan 1999),and based on the oxidation of central pyran ring,flavonoids can be categorized as flavonols,flavones,flavanonols,flavanones,flavan-3-ol,anthocyanidins,isoflavone,and proanthocyanidins(Hemingway 1989).
| 图表编号 | XD0047428900 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.20 |
| 作者 | Muhammad Khalid、Saeed-ur-Rahman、Muhammad Bilal、HUANG Dan-feng |
| 绘制单位 | School of Agriculture and Biology,Shanghai Jiao Tong University、School of Agriculture and Biology,Shanghai Jiao Tong University、School of Life Science and Food Engineering,Huaiyin Institute of Technology、School of Agriculture and Biology,Shanghai Jiao Ton |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 4 Sources of flavonoid compounds and their antifungal activities”的人还看了
-
![表4 盐孢菌属次级代谢产物与对应的生物合成基因簇[16]Table 4 Compounds and their associated BGCs (biosynthetic gene clusters) detected in Salinis](//bookimg.mtoou.info/tubiao/gif/AJSH201805007_37300.gif)
- 表4 盐孢菌属次级代谢产物与对应的生物合成基因簇[16]Table 4 Compounds and their associated BGCs (biosynthetic gene clusters) detected in Salinis
![表4 盐孢菌属次级代谢产物与对应的生物合成基因簇[16]Table 4 Compounds and their associated BGCs (biosynthetic gene clusters) detected in Salinis](http://bookimg.mtoou.info/tubiao/gif/AJSH201805007_37300.gif)