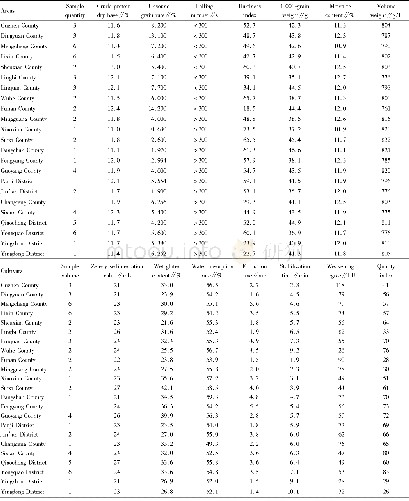
《Table 1.Properties of different samples.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction over molybdenum carbide nanoparticles confined inside single-walled carbon nanotubes》
aDetermined by inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectrometry(ICP–OES,PerkinElmer ICP-OES 7300DV).bMeasured from TEM images.cDetermined by N2adsorption/desorption,using Brunner-Emmett-Teller(BET)method.
The HRTEM shows that the MoCx@SWNTs exhibits much smaller MoCxparticles of 2.9 nm than that of MoCx/SWNTs(6.5 nm,Fig.1 and Table 1).It was reported previously that the particle size of Mo Cx-based electrocatalysts could play a decisive role in their catalytic activity for HER[36–38].For example,breaking down the micro-sized MoCxto various nanostructures(e.g.nanooctahedrons,nanowires,nanoparticles)had been demonstrated to exhibit a significant effect on the HER activity[19,38–40].Furthermore,the activity can be further enhanced by decreasing the size of MoCxat the nanoscale.For example,Nakanishi and co-workers reduced the size of molybdenum carbonitride(MoCN)materials from hundreds of nanometers to 20–30 nm by utilizing a CO2-emission assisted synthesis protocol,which consequently decreased the onset potential of HER from 90 to 50 mV[40].Liu and coworkers reported that the Mo Cxcatalyst with particle sizes of 10–15 nm exhibited 3 times higher current density at an overpotential of 200 mV than that of20–25 nm[38].Zou and co-workers demonstrated that reducing the size of MoCxparticles from 7.3 to 3.6 nm could significantly enhance the HER activity[20].A further reduction of MoCxsize from 1.5–4.5 nm to 1–3 nm by decreasing the annealing temperature could also improve HER activity,as demonstrated by Wang’s group[41].Therefore,the significantly smaller size of the encapsulated MoCxNPs could be one of the reasons for the higher activity of Mo Cx@SWNTs than MoCx/SWNTs since smaller particles not only provide a larger amount of catalytic sites but also facilitate the access of electrolytes thereby enable rapid mass and charge transfer.
| 图表编号 | XD0042896700 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.01 |
| 作者 | Tingting Cui、Jinhu Dong、Xiulian Pan、Tie Yu、Qiang Fu、Xinhe Bao |
| 绘制单位 | State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences、University of Chinese Academy of Sciences、State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences、University |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |