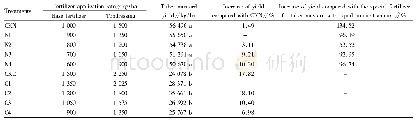
《Table 3.Effects of different inoculation treatments on rice samples.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Infection and Colonization of Pathogenic Fungus Fusarium proliferatum in Rice Spikelet Rot Disease》
Data are Mean±SD(n=3).Different lowercase letters in the same column refer to significant differences at the 5%level.
After inoculated with the Fp-GFP11 strain,23.33%of samples showed a small amount of hyphae colonizing on the outer surfaces of the lemma and palea at 24HAI(Fig.4-A and Table 1),indicating that pathogens can colonize the rice spikelet surface.The hyphae colonized on the outer surfaces(Fig.4-B)and inner surfaces(Fig.4-C)of both the lemma and palea at 36HAI,confirming that the pathogen had the ability to penetrate the lemma and palea.Furthermore,the infection rate of the lemma and palea were alsosignificantly increased(Table 1).Then,the hyphae were found to penetrate the anther epidermis(Fig.4-D)and extend between the pollen cells in the anthers at48 HAI(Fig.4-E),with 23.33%of the stamens infected(Table 1).The hyphae penetrated and damaged the pollen cells,which were deformed and ruptured at 60 HAI(Fig.4-F).The hyphae also extended to the pistils with the pollen cells(Fig.4-G)and 23.33%of the pistils was infected(Table 1).Finally,the anthers were observed to be completely infected by the mycelial network at 72 HAI,and more internal pollen cells were damaged(Fig.4-H).The pathogen primarily affected the pollen cells in the anthers and had no obvious infection effects on the other floral organs.Severe infections during this stage would lead to the death of the rice spikelets,and would have significant influences on the fertility and seed-setting rate of rice.
| 图表编号 | XD0040097300 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.28 |
| 作者 | SUN Lei、WANG Ling、LIU Lianmeng、HOU Yuxuan、XU Yihua、LIANG Mengqi、GAO Jian、LI Qiqin、HUANG Shiwen |
| 绘制单位 | College of Agronomy, Guangxi University、State Key Laboratory of Rice Biology, China National Rice Research Institute、State Key Laboratory of Rice Biology, China National Rice Research Institute、State Key Laboratory of Rice Biology, China National Rice Res |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 3.Effects of different inoculation treatments on rice samples.”的人还看了
-

- 表3 不同菌株处理对干旱胁迫下金钗石斛可溶性糖含量的影响Table 3 Effects of different strains treatment on soluble sugar content of Dendrobium nobile
-
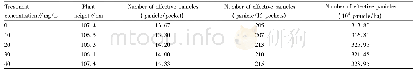
- Table 1 Effects of different treatments on rice plant height and number of effective panicles per unit area