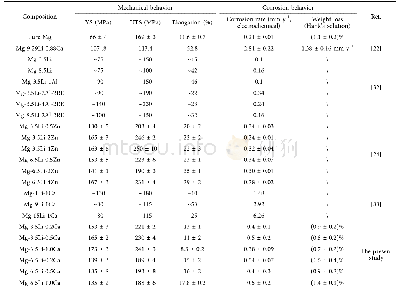
《Table 4 Summary of the mechanical and corrosion behavior of reported Mg-Li based alloys for biomedi
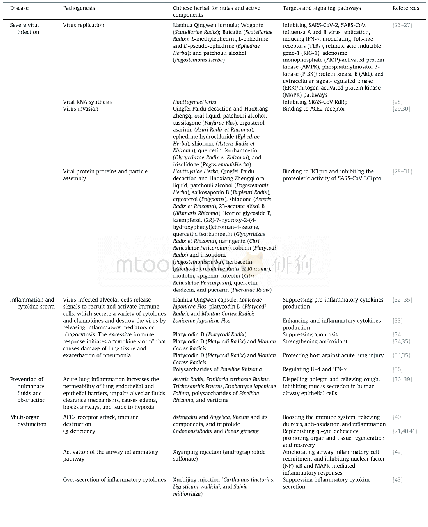
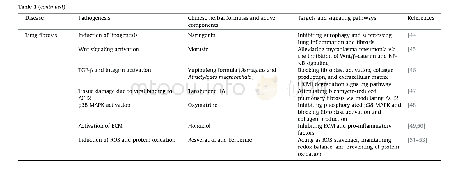
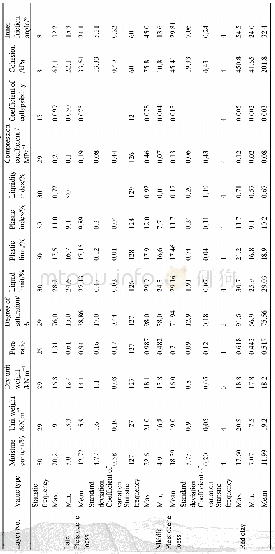
Upon examination of the results presented herein,it is clear that both Li and Ca strongly influence the mechanical and corrosion behavior of the alloys.Table 4summarizes the mechanical and corrosion behavior of recently reported Mg-Li based alloys developed for biomedical applications,against pure Mg used as a comparison.The addition of Li leads to large variations in mechanical properties and elongation,which makes it possible to tailor the mechanical properties of the alloys for different target applications.It is well documented that the addition of Li influences the crystal structure of Mg-Li based alloys[34].According to the summary,generally,the addition of Li results in less strength but higher elongation,while the addition of other alloying elements can increase strength due to solid solution strengthening and precipitation strengthening effects.In our study,we chose the most naturally abundant metallic element in the human body,Ca,with a view to improving implant mechanical performance,while minimizing adverse effects[22].As biodegradable metals,current MgLi-Ca alloys especially the Mg-3.5Li-0.5Ca and Mg-3.5Li-1.0Ca show favorable degradation qualities and comparable corrosion behavior,when compared to pure Mg counterparts.Furthermore,the reported Li2CO3protective layer provides an alternative strategy to other biodegradable Mg alloys to achieve better corrosion resistance[9,22,24].
| 图表编号 | XD0039960300 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.02.01 |
| 作者 | 夏丹丹、刘洋、王思仪、曾荣昌、刘云松、郑玉峰、周永胜 |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology、Department of Materials Science and Engineering, College of Engineering, Peking University、Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatolog |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 4 Summary of the mechanical and corrosion behavior of reported Mg-Li based alloys for biomedical application”的人还看了
-
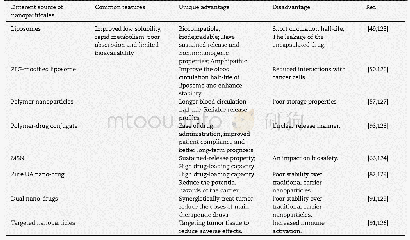
- Table 5–Summary of the differences,advantages,and disadvantages of different type nanosystems of UA in cancer therapy.
-
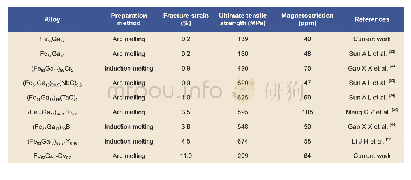
- Table 4:Summary of magnetostrictive and mechanical properties for third elements or carbides doped Fe-Ga polycrystalline
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式