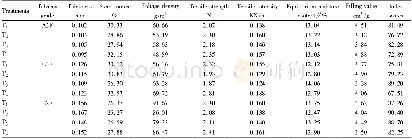
《Table 2 Properties of 1 and 2 and comparison with TNT, RDX, and HMX》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《多齿五唑N_5~-的自组装纳米含能配位聚合物(英文)》
a) Recalculated from low-temperature X-ray densities(ρ=ρT/ (1+αV (298–T0)) ;αV=1.5×10-4K-1) .b) Nitrogen content.c) Oxygen balance.d) Calculated heat of formation.e) Thermal decomposition temperature(onset)under nitrogen gas(DSC,5°C min-1).f)
Heat of detonation(Q),detonation velocity(D),and detonation pressure(P)are pivotal parameters for energetic CPs.On the basis of the largest exothermic principle proposed by Kamlet-Jacobs(K–J)[37],We employed a widely used empirical method[38,39]proposed by Pang and coworkers[40]to investigate the detonation properties of metal-containing energetic CPs.The detonation reactions of CP 1 and 2 are described by Equation S5,6,and the detonation properties are calculated by K–J equations(see Supporting Information).As shown in Table 2,the nitrogen contents(>66%)and heats of formation(>800 k J mol-1)for the two CPs are much higher than those of the traditional energetic materials(TNT,RDX,and HMX).But only the heat of detonation for CP 2(1.65 kcal g-1)is higher than those of TNT,RDX,HMX,and CL-20(about 1.5 kcal g-1).The D and P of CP2 are calculated to be 7,863 m s-1and 26.44 GPa,respectively,which are slightly higher than TNT.The poor detonation performance of CP 1 is attributed to their low density(<1.3 g cm-3)caused by porous structure.From another point of view,this porous structure may hold other small energetic materials and improve the energetic performance.
| 图表编号 | XD0039959300 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.01 |
| 作者 | 王鹏程、许元刚、王乾、邵艳丽、林秋汉、陆明 |
| 绘制单位 | School of Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology、School of Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology、School of Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology、School of Chemical Engin |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 2 Properties of 1 and 2 and comparison with TNT, RDX, and HMX”的人还看了
-
- Tab.2 Comparison of clinical manifestations between survivors and deaths in DM-ILD patients with anti-MDA5 antibody posi