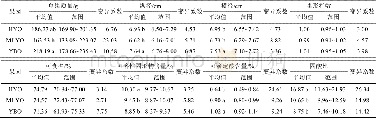
《Table 1 Datasheet of the extraction yield from different hydrocarbon sources with and without hydro
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《The scientific connotation of oil and gas formations under deep fluids and organic-inorganic interaction》
As a result of the high heat evolution of the Paleo-oil reservoir or the biodegradation due to the exposure at the surface,the reservoir bitumen widely exists in the ancient strata of many basins in China and around the world.Bitumen is rich in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polymer groups,and it can also be activated by hydrogenation for hydrocarbon generation,which in turn is similar to heavy oil.Since deep fluids carry energy,hydrogen-rich fluids,a large number of catalysts,and other elements,they can hydrogenate the reservoir bitumen.Hence,activating the capacity of hydrocarbon regeneration for reservoir bitumen and the inert carbon of the reservoir bitumen to generate hydrocarbons.The catalytic hydrogenation pyrolysis can furthest increase the release yield of biomarkers of the covalent bonding chain hydrocarbon.In turn,the aforementioned increases the amount of hydrocracking product by 25.7 to 456times more(Table 1;Fang et al.,2014)without affecting its stereoisomerization characteristics(Love et al.,1995;Liao et al.,2012).The amount of hydrocracking product depends on the thermal evolution degree of the reservoir bitumen and the organic matter type(Bishop et al.,1998).As a result,hydrogenation not only activate inert bitumen carbon to generate hydrocarbons alone,it also provides biomarkers of hydrogenated products that can be used for the oil-source correlation at the high evolved stage and the analysis of paleo-sedimentary environments(Liao et al.,2012).The hydrogenation reaction of coal is the synthesis of heavy oil,medium oil,gasoline,and natural gas by hydrogenation reaction on high volatile bituminous coal under the conditions of high temperature and pressure.
| 图表编号 | XD0034780800 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.03.01 |
| 作者 | Quanyou LIU、Dongya ZHU、Qingqiang MENG、Jiayi LIU、Xiaoqi WU、Bing ZHOU、Qi FU、Zhijun JIN |
| 绘制单位 | State Key Laboratory of Shale Oil and Gas Enrichment Mechanisms and Effective Development、Structure & Sedimentary Reservoir Laboratory, Petroleum Exploration & Production Research Institute,SINOPEC、State Key Laboratory of Shale Oil and Gas Enrichment Mech |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1 Datasheet of the extraction yield from different hydrocarbon sources with and without hydrogenation”的人还看了
-

- Table 1 Extraction efficiency of uranium from alkali residue by supercritical fluid under different conditions
-
- 表3 冰糖橙果实的品质指标Table 3 Variation of fruit quality of bingtang orange collected from different yield orchards
-

- 表3 不同微波功率处理刺梨的提取率Table 3 Extraction rate of polysaccharide from R.roxburghii under different microwave power





