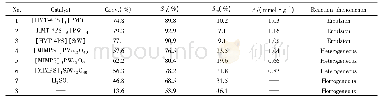
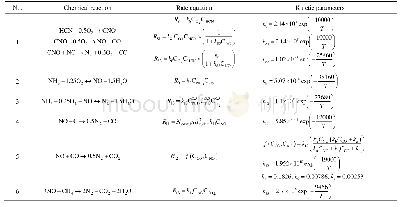
《Table 5 Catalytic reduction of NOx over vanadium-based catalysts》
Rencently,V-based catalysts have gained increasing importance,and the results were summarized in Table 5.Cha et al.[24]prepared TiO2 nanoparticles by chemical vapor phase condensation(CVC)method,and thensynthesizedV2O5/CVC-TiO2usingthe impregnation method.V2O5/P25-TiO2(a mixed crystal type of Ti O2,and the mass ratio of anatase to rutile is about 71/29)was obtained by loading the same amount of V2O5 on commercial P25-TiO2.As shown in Fig.5[20],to achieve the NOx conversion rate of 96%,the required operating temperature of the 7wt%V2O5/CVC-TiO2catalyst was about 50℃lower than that of the 5wt%V2O5/CVC-TiO2catalyst.At200℃,the V2O5/CVC-TiO2 catalysts with varying concentrations of V2O5 showed sufficient NOx conversion,while the NOx conversion efficiencies of the V2O5/P25-TiO2catalysts with the same V2O5 concentrations were insufficient.It was proposed that the V2O5/CVC-TiO2catalysts had more anatase phase TiO2,a higher specific surface area,and better dispersion than the V2O5/P25-TiO2 catalysts.The characterizations revealed that V2O5/CVC-TiO2 exhibited larger specific surface area,higher dispersion,and more surface oxygen.
| 图表编号 | XD0033430900 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.04.01 |
| 作者 | 宁汝亮、刘霄龙、朱廷钰 |
| 绘制单位 | 贵州大学化学化工学院、中国科学院过程工程研究所湿法冶金清洁生产技术国家工程实验室、中国科学院过程工程研究所湿法冶金清洁生产技术国家工程实验室、贵州大学化学化工学院、中国科学院过程工程研究所湿法冶金清洁生产技术国家工程实验室、中国科学院城市环境研究所区域大气环境卓越中心 |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式