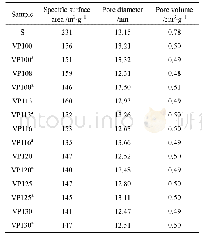
《Table 2 Pore size and specific surface area for different samples》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Influence of Cr~(3+) Concentration on SO_2 Removal over TiO_2 Based Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes》
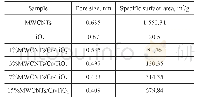
The enhancement of the adsorption capacity of15%MWCNTs/Cr-TiO2 might be attributed to a combination of factors.The XPS analysis confirmed the presence of surface defects due to the partial transfer of Ti4+to Ti3+.These surface defects acted as adsorption sites for SO2.Moreover,the Crn+inside TiO2 could serve as both the electron and hole traps.Crn+trapped electrons and holes to form Cr(n-1)+and Cr(n+1)+and to generate superoxide or hydroxyl radicals.The improved adsorption ability of 15%MWCNTs/CrTiO2 might be ascribed to modifications of the surface structures.Given that the atom ratio of Cr to Ti detected on the sample surface was less than the theoretical value on 15%MWCNTs/Cr-TiO2,a portion of Cr species(Cr3+and Cr6+)were believed to be incorporated into the TiO2lattice.The XRD analysis indicated that the crystallite size of the samples decreased in the Cr-doped samples as compared with those in pure TiO2.Table 2 shows the specific surface area and pore size of MWCNTs,TiO2,and MWCNTs/Cr-TiO2(1%,3%,7%,and 15%)obtained by the BET analysis.A smaller pore size induced a growth of the specific surface area,resulting in more structural defects and surface absorption sites.In other words,the amount of surface oxygen vacancies increased on the sample surface.In view of the strong oxidizing properties of Cr3+and Cr6+[32],as the Cr content increased,the oxidizability of the sample increased,resulting in an increased sulfur capacity of the sample.Therefore,a high Cr molar fraction in MWCNTs/TiO2within the range of 1%–15%(Cr:Ti)could increase the SO2 adsorption capacity and adsorption rate of the sample.
| 图表编号 | XD0029185600 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.03.30 |
| 作者 | Yang Yanchun、Jia Fengrui、Jian Weiwei、Zhang Shaopeng、Ma Danzhu、Liu Guangxin |
| 绘制单位 | College of Petroleum Engineering, Liaoning Shihua University、College of Petroleum Engineering, Liaoning Shihua University、College of Petroleum Engineering, Liaoning Shihua University、College of Petroleum Engineering, Liaoning Shihua University、College of |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 2 Pore size and specific surface area for different samples”的人还看了
-

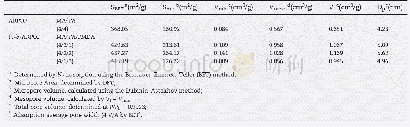
- Table 1–Comparison of the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area, pore size and pore volume of the different samples.