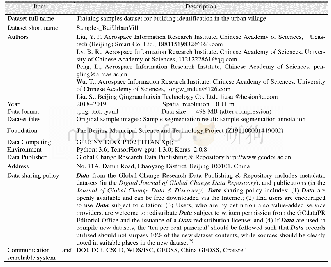
《Table 1 Summary of the base composition of the cp genomes of four Salvia species.》
RNA editing participates in plastid transcription regulation,which can enrich transcription and protein diversity[43–45].In this study,35 genes of the four Salvia cp genomes were predicted for their potential RNA editing sites.A total of 43 RNA editing sites were predicted;of these,37 are common sites of the four species(Table S4 in SD).Of the 35 genes,16—including atpA,atpB,clpP,petD,petG,petL,psaB,psaI,psbB,psbE,psbF,psbL,rpl23,rpoC1,rps8,and ycf3—were not measured for their potential RNA editing sites.The rps16 gene was not measured for its potential RNA editing sites in S.japonica,but one potential RNA editing site was observed in the three other species.Of the 43 potential RNA editing sites,11 were observed at the first position of the corresponding codon and 32 were observed at the second position.No potential RNA editing site was observed at the third position,and the base conversion type is all C to T.This result is similar to those of other land plants[46,47].The conversion of amino acids from Ser to Leu occurs most frequently,while the conversions from Pro to Ser and Thr to Ile occur least frequently.
| 图表编号 | XD00131544900 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.10.01 |
| 作者 | 梁从莲、王磊、雷隽、段宝忠、马维思、肖水明o、齐海军、王振、刘尧奇、沈晓凤、郭帅、胡灏禹、徐江、陈士林 |
| 绘制单位 | College of Pharmacy, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)、Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences、State Key Laboratory of Innovative Natural Medicine and TCM Injections, Jiangxi Qingfeng Pharmace |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1 Summary of the base composition of the cp genomes of four Salvia species.”的人还看了
-

- able Gene number and CDS nucleotide composition of the cp genomes of the four Salvia species.SpNuogeCbAT
-

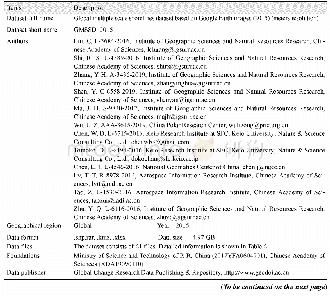
- Table 1 Metadata summary of“Bayberry tree recognition dataset based on the aerial photos and deep learning model”
-

- Table 1 Metadata summary of“Bayberry tree recognition dataset based on the aerial photos and deep learning model”
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式