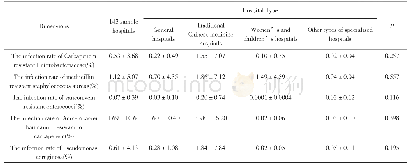
《Table 3 Comparative studies among different techniques of biliary drainage》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Comprehensive review on EUS-guided biliary drainage》
PS:Prospective study;RS:Retrospective study;Rev:Review;EUS-BD:Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided biliary drainage;EUS-HGA:Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided hepatogastric anastomosis;EUS-CDS:Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided choledochoduodenostomy;EUS-RV:En
PTBD represents a rescue procedure for ERCP failure.The technical success rate of PTBD is over 95%with a 33%or higher overall adverse event rate including bleeding,infection,dislodgement,biliary leak,and tract seeding[2].Moreover,this technique can be uncomfortable for the patient due to an external drainage catheter and is contraindicated with ascites or multiple liver metastasis.EUS-BD has become an evolving alternative to PTBD with a better clinical success rate(OR:0.45),fewer adverse events(OR:0.23),and fewer reinterventions(OR:0.13)[16](Tables 3 and 4).EUS biliary drainage can be achieved by puncturing the intrahepatic duct in the III segment(intrahepatic approach)and inserting an HGA stent,advancing a guidewire across the stricture and the papilla to complete an antegrade stent placement,or by puncturing the common bile duct,or the gallbladder(extrahepatic approach)with CDS or GBD(Figure 2).When the papilla is accessible,puncturing the biliary tree(intrahepatic or extrahepatic)and inserting the guidewire into the small intestine to cannulate with the rendez-vous technique(EUS-RV)represents the most appropriate and safe route.
| 图表编号 | XD0058772900 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.05.16 |
| 作者 | Raffaele Salerno、Sophia Elizabeth Campbell Davies、Nicolò Mezzina、Sandro Ardizzone |
| 绘制单位 | Gastroenterology and Digestive Endoscopy Unit,ASST Fatebenefratelli Sacco-Department of Biochemical and Clinical Sciences “L. Sacco”,University of Milan、Hospital Pharmacy,ASST Fatebenefratelli Sacco,Piazza Principessa Clotilde、Gastroenterology and Digesti |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |