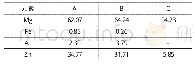
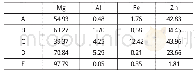
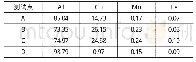
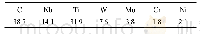《Table 2:EDS analysis results of points in Fig.3》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Effects of trace Cr on as-cast microstructure and microstructural evolution of semi-solid isothermal heat treatment ZC61 magnesium alloy》
In this work,to further confirm compositions and demonstrate subtle characteristics,the alloys have undergone EDS microanalysis considering the similarity of the microstructures after adding Cr element.The SEM high-magnification micrographs are shown in Fig.3 and the corresponding EDS results are shown in Table 2.It can be seen from Fig.3 that the eutectic phases of these alloys show the thin sheet-like and fishbone characteristics,and the eutectic phases are mainly consisted of white and dark gray compounds.Especially when Cr is added,white eutectic compounds relatively reduce,and the amount of thin sheet-like microstructures increase.However,the Cr element is still not detected by EDS(Table 2)due to the low solubility of Cr in Mg according to binary Mg-Cr phase diagram[21].But this does not mean the Cr element does not exist,because Buha[16]certified that a trace element Cr with content of 0.05at.%did dissolve in the magnesium lattice in the presence of Zn in the Mg-6Zn-0.2Cr alloy.For ZC61 and ZC61-0.1Cr alloys,white phases isolated in the matrix(marked C and F)and lamellar dark gray phases(marked A,B and E)all contain Mg,Zn and Cu atoms,so these compounds are consisted ofα-Mg+MgZn2+CuMgZn combined with XRD results;and dark gray phases(marked D)circled by blue where the atomicratio of Mg to Zn without Cu approaching 3:1 is determined asα-Mg+Mg Zn2 mixed phases.
| 图表编号 | XD0049759000 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.01 |
| 作者 | Xiao-feng Huang、Ya-jie Ma、Qiao-qiao Zhang、Lang-lang Wei、Jian-qiao Yang |
| 绘制单位 | State Key Laboratory of Advanced Processing and Recycling of Nonferrous Metals, Lanzhou University of Technology、State Key Laboratory of Advanced Processing and Recycling of Nonferrous Metals, Lanzhou University of Technology、State Key Laboratory of Advan |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |