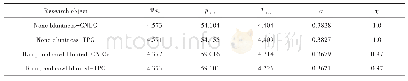
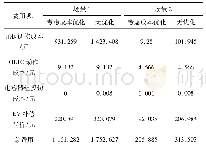
《Table 4 Experimental results in different scenarios performed with fractured models》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Viscous fingering and its effect on areal sweep efficiency during waterflooding: an experimental study》
As it was mentioned earlier,two experiments were performed with a fractured model.The perpendicular fracture acted such as a distributor,which led to higher displacement efficiency.When water exited from the perpendicular fracture,several parallel short fingers formed which would improve the areal sweep efficiency.The parallel fracture acted in order to join fingers.In this circumstance,a single finger was formed and a considerable area of the model remained unswept.This led to poor sweep efficiency.More unswept region remained in the model if the perpendicular fracture was not located behind the parallel one.In the second water flooding which water first entered the parallel fracture,lower sweep efficiency and earlier breakthrough were observed at the same injection volume compared with other case as can be seen from Fig.14 and Table 4.The onset and growth of fingers in the presence of fractures are also shown in Figs.15a–d and 16a–d.
| 图表编号 | XD0042157000 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.02.01 |
| 作者 | Zahra Kargozarfard、Masoud Riazi、Shahab Ayatollahi |
| 绘制单位 | Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) Research Centre, IOR-EOR Research Institute, Shiraz University、Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) Research Centre, IOR-EOR Research Institute, Shiraz University、Department of Petroleum Engineering, School of Chemical and Petroleum Eng |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |