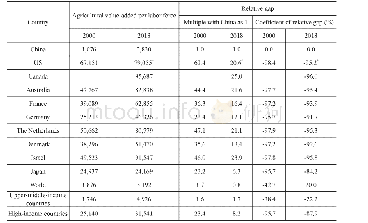
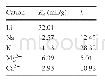
《Table 2 Force field types for adsorbents》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Review of Molecular Simulation Method for Gas Adsorption/desorption and Diffusion in Shale Matrix》
The force field describes the relationship between the adsorbent and the adsorbate as well as the adsorbate and adsorbate.The type of potential for intermolecular interaction chosen in molecular dynamics simulations can affect the results of adsorption amount and diffusion coefficient obtained from GCMC and MD,respectively.For example,when the values of the potential for intermolecular interaction exceed the actual values,the values of the predicted adsorption amount are higher compared to that using the actual values.On the contrary,the values are lower compared with that using the actual values.Those phenomena are similar to CO2/CH4 gas separation in Cu-BTC[62].For the diffusion calculated by MD,the variation of diffusion coefficient is not only related to the values of the potential for intermolecular interaction,but also related to the kinds of matrix,adsorbate and depth of the shale matrix[57].The diffusion coefficient is not monotonic relationship with the depth.Therefore,the sensitivity of diffusion values is difficult to be determined[57].In order to validate the accuracy of the force field parameters used in GCMC and MD model,there are preliminary experimental data of adsorption amount available which should be compared with the numerical simulations,such as CH4 adsorption in montmorillonite[57],CH4 and CO2 adsorption in K-illite[43].The contents of CH4,CO2,N2,H2O,C2H6,and C3H8 in the shale gas are treated as the adsorbates.The force field parameters of adsorbates are summarized in Table 1.
| 图表编号 | XD0039670300 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | |
| 作者 | WANG Hui、QU Zhiguo、YIN Ying、BAI Junqiang、YU Bo |
| 绘制单位 | School of Aeronautics, Northwestern Polytechnical University、MOE Key Laboratory of Thermo-Fluid Science and Engineering, School of Energy and Power Engineering, Xi'an Jiaotong University、MOE Key Laboratory of Thermo-Fluid Science and Engineering, School |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |