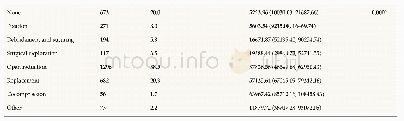
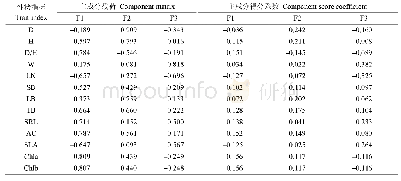
《Table 3.The RMSE, RMAE and RMB scores for radar-derived hourly rainfall before and after correction
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《"Evaluating the Algorithm for Correction of the Bright Band Effects in QPEs with S-, C-and X-Band Dual-Polarized Radars"》
The radar-derived hourly rainfall was compared with rain-gauge observations(Fig.8)for the three events from the C-band radar at 3.4?tilt at 1200–1300 UTC 4 August2013,X-band radar at 2?tilt at 0500–1100 UTC 27 October 2016,and S-band radar at 2.4?tilt at 1400–1800 UTC 31March 2017.The radar-based QPEs from the uncorrected reflectivity significantly overestimated the rainfall in the brightband areas(Figs.8a,d and g).The QPE overestimations in the bright-band areas were reduced after the reflectivity fields were corrected by the AVPR(Figs.8b,e and h)and AVPR+CC(Figs.8c,f and j)schemes.Figure 8 also shows the scatter points of rainfall data that had no contamination of bright bands.The corrected bright-band area rainfall shows a similar distribution as those of no contamination.Three statistics(RMSE,RMAE and RMB)were calculated and listed in Table 3 for the radar-derived hourly rainfall with respect to the surface rain-gauge observations,focusing only on the bright-band affected areas.Figure 9 shows the scatter points of rainfall data that had contamination of bright bands at different tilts.The rainfall from the uncorrected and corrected reflectivity shows a similar distribution.In general,reflectivity corrections based on the AVPR and AVPR+CC schemes had positive impacts in reducing the overestimation of Z–R relationship–based QPEs in the bright-band areas.Furthermore,the AVPR+CC correction scheme eliminated more overestimation of QPE than the AVPR correction scheme,as the reflectivity in the bright-band areas was further reduced by the AVPR+CC scheme(Figs.7c,f and i versus Figs.7b,e and h).
| 图表编号 | XD0030264700 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.01.10 |
| 作者 | Yang CAO、Debin SU、Xingang FAN、Hongbin CHEN |
| 绘制单位 | Key Laboratory of Middle Atmosphere and Global Environment Observation,Institute of Atmospheric Physics,Chinese Academy of Sciences、College of Electronic Engineering,Chengdu University of Information Technology、Sichuan Meteorological Disasters Prevention |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |