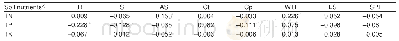《Table 3 Correlation coefficients of meteorological factors and soil temperature》
The results showed that soil temperature in alpine and high-altitude areas had a similar periodic trend of sine and cosine,with a maximum amplitude of 15.7oC,which is consistent with the results on soil temperature variation trends in other regions of China[15-18],but slightly different in oscillation period and amplitude.Qi et al.[19]monitored 22stations on the Changtang Plateau,and compared with this paper,the difference in diurnal and monthly changes was 1.2-1.6oC.The differences may be caused by different time scales of data monitoring,differences in latitude and longitude or surface vegetation[20].In January,April,July and October,the soil temperature showed a law of large difference in winter and small difference in summer,the main reason is that the sunshine duration is longer in summer than in winter in Nagqu region,and the energy received by the soil is different.In addition,the soil type is alpine meadow,with more gravel under the soil,and the specific heat capacity of the soil is small,leading to a large change in the day-night temperature.On the spatial scale,the mean temperature of each layer in soil showed a tendency of increasing first and then decreasing with increasing soil depth.In four special months,the temperature amplitude of different soil layers decreased with the increase of depth,and the lag time of peak-valley variation become longer with the increase of depth,the lag time increased by about 1 h for every 10 cm increase of depth.
| 图表编号 | XD00206979800 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2020.06.25 |
| 作者 | 杨洪波、于晓丹、付海美、李慧婷、赵晋灵、徐娓 |
| 绘制单位 | 亿利生态修复股份有限公司、亿利生态修复股份有限公司、北京市理化分析测试中心、亿利生态修复股份有限公司、亿利生态修复股份有限公司、亿利生态修复股份有限公司 |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 3 Correlation coefficients of meteorological factors and soil temperature”的人还看了
-
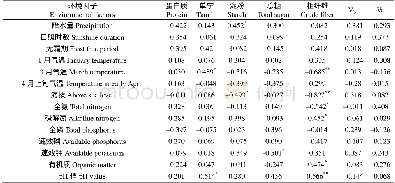
- 表3 环境因子与竹笋营养成分的偏相关系数Table 3 The partial correlation coefficients of environmental factors and nutritional components of
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式