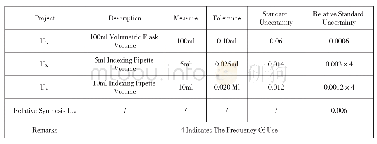
《Table 4Consequences of APLs during cholecystectomy by involved organ/structure.a》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Detecting accidental punctures and lacerations during cholecystectomy in large datasets: Two methods of analysis》
a Compared to cholecystectomy without APLs,with mortality of 0.31%,LOS of 3(2–5)days,median charges of$21.30 K(13.56 K–34.45 K).APLs of peritoneum and mesentery,bladder,diaphragm and spleen were omitted due to low number of cases and non-signifi
Analysis of 9884 clinically significant APLs(marked by CM;Table 2)revealed that the most commonly injured structures during cholecystectomy are the small and large intestines(42.95%of clinically significant APLs).Vascular injuries comprised 28.22%of these injuries and among the most severe complications 21.34%experienced bile duct injury and 6.18%experienced clinically significant liver lacerations.Among the remainder of clinically significant APLs were injuries of the peritoneum and mesentery(1.69%),stomach(1.20%),bladder(0.48%),diaphragm(0.36%)and spleen(0.08%).
| 图表编号 | XD0020453700 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.10.15 |
| 作者 | Artem Shmelev、Anne M Sill、Gopal C Kowdley、Juan A Sanchez、Steven C Cunningham |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Surgery, Saint Agnes Hospital and Cancer Center、Department of Surgery, Saint Agnes Hospital and Cancer Center、Department of Surgery, Saint Agnes Hospital and Cancer Center、Department of Surgery, Saint Agnes Hospital and Cancer Center、Departm |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 4Consequences of APLs during cholecystectomy by involved organ/structure.a”的人还看了
-
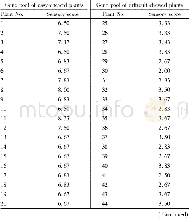
- Table 2Sensory evaluation of Chinese cabbage plants involved in the verification of RAPD primer OPA-06
-
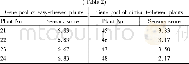
- Table 2Sensory evaluation of Chinese cabbage plants involved in the verification of RAPD primer OPA-06