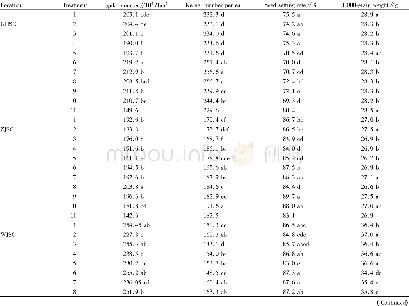
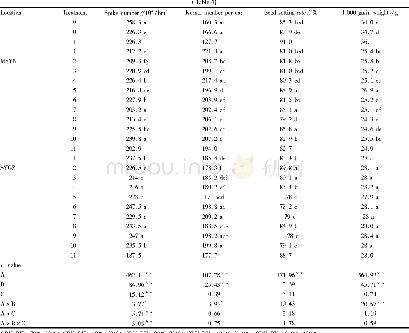
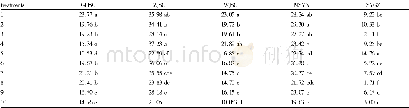
《Table 3 Amounts of different K forms and cumulative non-exchangeable K released in different media
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《"Potassium forms in calcareous soils as affected by clay minerals and soil development in Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province, Southwest Iran"》
Note:Sur S,surface soil;Sub S,subsurface soil;–,no data.
The results in Tables 3 and 4 showed that soluble K varied in pedons,although it was higher in surface soils than in subsurface soils and was significantly correlated with OC and exchangeable K(Pearson correlation coefficients of 0.465 and 0.468,respectively).Soluble K did not show significant correlation with other soil physical-chemical properties(CEC,clay content and CCE),clay minerals(illite,smectite,vermiculite and smectite+vermiculite),and other two K forms(non-exchangeable and structural).Soluble K can be affected by K fertilizers,plant uptake,replacement by other K forms,and sampling time.There are several K minerals in soils,but availability of the K soluble form for plant growth is usually limited(Hayashi et al.,2014).Soluble K was the smallest part of total K in surface and subsurface soils(accounting for 0.1%of total K).In the study area,exchangeable K accounted for 3.3%of total K in surface soils and2.2%in subsurface soils.Exchangeable K was higher in surface soils than in subsurface soils.The largest amount of exchangeable K in the study area was in surface soils of pedons 36(Mollisols),49(Alfisols),33(Alfisols),46(Mollisols),2(Mollisols)and 39(Vertisols).In these pedons,OC content was high and smectite was a predominant mineral.In addition,lower amount of exchangeable K was found in subsurface soils of pedons 7(Alfisols),29(Entisols),53(Entisols),13(Inceptisols),30(Inceptisols),11(Entisols)and 12(Inceptisols).These results revealed that poor-developed soils,except pedon 7 due to the presence of Gachsaran formation(palygorskite as the predominant mineral),had less exchangeable K.In these soils,the main minerals were illite,chlorite,and palygorskite.The relationship between different forms of K is generally influenced by the type of clay and soil texture(Nabiollahy et al.,2006).Moreover,exchangeable K is retained by expanding clay minerals(Sharpley,1989).Bhonsle et al.(1992)reported that the largest amount of exchangeable K is in soils with smectite as the main mineral.Exchangeable K is held throughout electrostatic charges present on organic matter and clay particles(Conyers and Mc Lean,1969).Enriched sources of illite in the surrounding areas and alteration of biotite in surface soils due to daily and seasonal variations of moisture and temperature resulted in illite decreased with increasing soil depth(Khormali and Abtahi,2003).Alteration of illite to smectite occurred in surface soils of Alfisols and other soils in humid regions.Compared to illite,smectite can be transformed and deposited into subsurface soils because smectite is in fine fraction,but the major reason could be due to the presence of a lot of smectite in parent materials which increases with increasing soil depth.
| 图表编号 | XD0020358500 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.04.01 |
| 作者 | Sirous SHAKERI、Seyed A ABTAHI |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Agriculture, Payame Noor University、Department of Soil Science, College of Agriculture, Shiraz University |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 3 Amounts of different K forms and cumulative non-exchangeable K released in different media of extraction in repr”的人还看了
-
- Table 1 Grain yield results of different test sites, different nitrogen amounts and different ratios of controlled-relea
-
- Table 2 Yield variance analysis results of different test sites, different nitrogen amounts and different ratios of cont
-
- Table 6 The agronomic efficiencies of nitrogen in different test sites, different amounts of nitrogen and ratios of cont
![表3 不同岩石性质的K、α值[1]Table 3 K andαvalues of different rock[1]](http://bookimg.mtoou.info/tubiao/gif/BASE201802034_11200.gif)