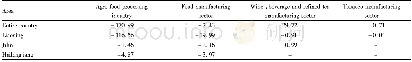《Table 2–Exosome-based small RNA delivery for the treatment of tumors.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Exosome-based small RNA delivery:Progress and prospects》
TGF-β1:transforming growth factorβ1;HLSCs:human adult liver stem cells.
Small RNAs are key regulators of gene expression in cancers[70].Given that exosomes are able to transport nucleic acids to target cells,interest is fast growing in utilizing exosomes as vehicles to deliver therapeutic nucleic acids for the treatment of cancers.As a natural RNA carrier in our bodies,exosomes have high stability in the circulation and intrinsic homing ability,which is therapeutically advantageous compared to conventional anti-tumor delivery systems[71].As a result,exosomes can help in the protection and specifically delivery of small RNAs to the targeted tumor cells when employed as therapeutic vehicles.In addition to the natural capacity to deliver RNAs,exosomes are non-viable,thus posing less risk of tumor formation[72].Moreover,in contrast to viral vectors,exosomes delivery is notably safe without the risk of insertional oncogenesis[72].Finally,the surface of exosomes may be modified to improve tumor-specific or even patient-specific capacity[73].The current utilization of exosomes in RNAi for cancer therapy mainly focuses on testing their capacity to target small RNAs to the“disease sites”,alter gene expression in certain diseases,and enhance genetic therapy.A summary of research articles tailoring exosomes as delivery vehicles of small RNAs for treatment of tumors is provided in Table 2.
| 图表编号 | XD00186251500 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.01.01 |
| 作者 | Mei Lu、Haonan Xing、Zhe Xun、Tianzhi Yang、Pingtian Ding、Cuifang Cai、Dongkai Wang、Xiaoyun Zhao |
| 绘制单位 | School of Pharmacy, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University、School of Pharmacy, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University、Institute of Metabolic Disease Research and Drug Development, China Medical University、Department of Basic Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pha |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 2–Exosome-based small RNA delivery for the treatment of tumors.”的人还看了
-
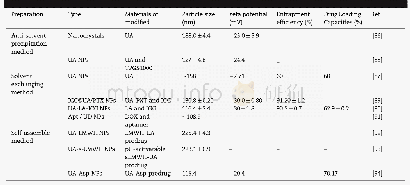
- Table 2–The preparation and characteristics of novel carrier-free based nano-drug delivery systems of UA.