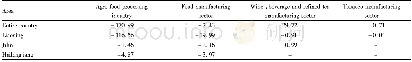《Table 1–Exosome-based small RNA delivery for the treatment of neurological diseases.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Exosome-based small RNA delivery:Progress and prospects》
RVG:rabies virus glycoprotein peptide;MOR:opioid receptor mu;VEGF:vascular endothelial growth factor;MSC:marrow stromal cell;HEK:human embryonic kidney.
Much progress has been made in utilizing exosomes to deliver small RNAs across the BBB during the past few years.An overview of current exosome-based small RNA delivery systems for the treatment of neurological diseases is shown in Table 1.Yang et al.[63],very recently performed a study employing brain endothelial exosomes to deliver si RNA across the BBB in zebra fish model of U87 glioblastoma.The in vitro and in vivo results showed that siRNA delivered by exosomes was efficiently transported across the BBB,significantly reduced VEGF gene level in brain neuronal glioblastoma-astrocytoma cells and inhibited the aggregation of xenograft brain tumors in zebrafish.These results indicated brain endothelial exosomes could deliver exogenous si RNA to the targeted site in the brain for the treatment of brain cancer.To improve the capacity of CNS-targeting,many studies engineered exosomes to express rabies virus glycoprotein peptide(RVG),a 29-mer peptide sequence that specifically binds to acetylcholine receptors expressed on neurological cells[69].Generally,targeting moieties could either be expressed in the donor cells or directly fused onto exosome membrane surface.Alvarez-Erviti and coworkers[15],provided the first proof-of-concept of exploiting the RNA-transporting capacity of modified exosomes for the delivery of exogenous si RNA across the BBB.Given that si RNA lacks efficient carriers to traverse the BBB,the study set out to target small RNAs delivery into the brain via exosomes.Targeting of nerve cells was achieved by fusing exosomal protein lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 2b(Lamp2b)to brain-specific RVG peptide.Targeting exosomes were subsequently loaded with si RNA by electroporation.After intravenously injection,siRNA was specifically delivered to neurons,microglia,oligodendrocytes in the brain,and led to specific knockdown of target gene in these regions.Furthermore,the ability of targeting siRNA to the brain via RVG-exosomes was further tested by the delivery of BACE-1 siRNA(targeting the enzymeβ-secretase,a therapeutic site in Alzheimer’s disease).Strong RNAi responses were observed with up to 60%mRNA and protein knockdown of BACE1.Of note,RVG-exosomes were shown to almost completely bypass liver,displaying minor or no immunogenicity even after repeated administration.This is a critical feature for developing RNAibased therapeutics.In a similar study by Liu et al.[65],neuronspecific RVG was also engineered onto exosome encapsulating siRNA via Lamp2b.The targeting exosomes were utilized to deliver opioid receptor mu(MOR)siRNA to the brain for the therapy of morphine addiction.After intravenously injection,MOR si RNA delivered by RVG-targeted exosomes strongly suppressed morphine relapse via down-regulation of MOR expression level in the brain.The results convincingly demonstrated that targeted RVG exosomes can efficiently and specifically deliver si RNA to the central nervous system for the therapy of drug relapse.
| 图表编号 | XD00186251800 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.01.01 |
| 作者 | Mei Lu、Haonan Xing、Zhe Xun、Tianzhi Yang、Pingtian Ding、Cuifang Cai、Dongkai Wang、Xiaoyun Zhao |
| 绘制单位 | School of Pharmacy, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University、School of Pharmacy, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University、Institute of Metabolic Disease Research and Drug Development, China Medical University、Department of Basic Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pha |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1–Exosome-based small RNA delivery for the treatment of neurological diseases.”的人还看了
-
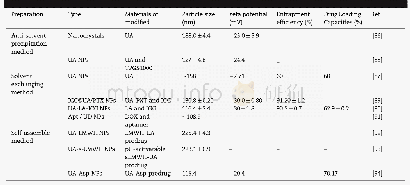
- Table 2–The preparation and characteristics of novel carrier-free based nano-drug delivery systems of UA.