《Table 1–Mean monthly and total rainfall (mm) during the study period in 2014/2015 and 2015/2016 at
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Genotype-by-environment interaction for grain yield among novel cowpea(Vigna unguiculata L.) selections derived by gamma irradiation》
Mean yield for the studied traits varied widely,from 0.74 to2.83 t ha-1.Table 3 shows the mean grain yields(t ha-1)of the34 cowpea mutant genotypes and their three parental lines in six environments in northern Namibia.AMMI analysis of variance revealed highly significant main effects(P<0.001)of genotypes,environments and their interactions(Table 4).Genotype,G×E interaction,and the AMMI model explained respectively 37.95%,33.83%,and 77.49%of the total observed variation.In contrast,interaction principal component axes IPCA1 and IPCA2 explained respectively 44.63%and 23.41%of the total variation.Genotype G9 was ranked first across all the test environments.Mutant lines G19 and G22,developed from the parent Nakare irradiated at 150 Gy,were among the high and stable yielders.Based on the AMMI biplot(Fig.1),acute angles were observed between vectors of genotypes G4,G5,and G15 and those of environments E1,E3,and E5.The acute angle between the lines that connect the biplot origin and environments E1 and E3,as well as E2,E4,and E6 showed their close relationships.Genotype G20 was the most stable,with an ASV of 0.08(Table 5).
| 图表编号 | XD0012324500 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.06.01 |
| 作者 | Lydia Horn、Hussein Shimelis、Fatma Sarsu、Learnmore Mwadzingeni、Mark D.Laing |
| 绘制单位 | African Centre for Crop Improvement,University of Kwa Zulu-Natal、Directorate of Research and Training,Plant Production Research,Ministry of Agriculture,Water and Forestry、African Centre for Crop Improvement,University of Kwa Zulu-Natal、Plant Breeding and |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 1–Mean monthly and total rainfall (mm) during the study period in 2014/2015 and 2015/2016 at three field sites.”的人还看了
-
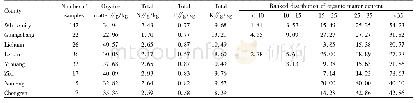
- Table 2 Mean contents of organic matter, total nitrogen, total phosphorus and total potassium in tobacco-planting soil i
-
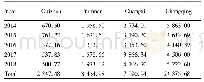
- Table 2 Comparison of the total import and export volume of fourprovinces and cities during 2014-2018