《Table 1–Summary of EST-SSRs identified in transcriptome sequences.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Development and validation of simple sequence repeat markers from Arachis hypogaea transcript sequences》
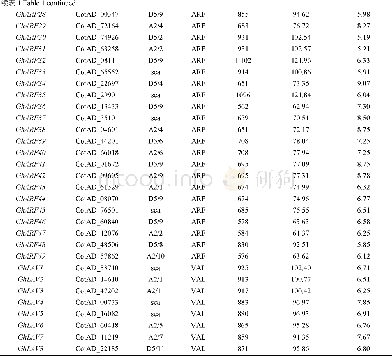
All 128,725 unigenes assembled de novo from the A.hypogaea transcriptome(NCBI Sequence Read Archive database,SRP061959)with a total length of 98.47 Mb were used to identify potential SSR loci using MISA.A total of 29,357potential SSRs were identified in 22,806 unigenes,with 4883unigenes containing more than one SSR locus(Table 1).The distribution density was one SSR locus per 3355 bp,and the number of repeat units ranged from one to six.The number of SSRs with each repeat motif varied widely.SSRs with mononucleotide repeat motifs were most abundant(19,065;64.94%),followed by tri-(5033;17.14%),di-(4927;16.78%),tetra-(303;1.03%),penta-(18;0.061%),and hexanucleotide(11;0.037%)repeat motifs(Table 1,Fig.S1).Additionally,1710 SSRs were present in compound forms(Table 1).The iteration number of repeat units in SSRs ranged from 4 to 22 and the occurrence frequencies of SSRs with different iteration numbers were unequal.The most common iteration number was 10(8467;28.84%),followed by 11(3959;13.49%),five(3634;12.38%)and six(3507;11.95%)(Table S3,Fig.S1) .For the SSRs with>10 repeat units,mononucleotide repeat motifs were most abundant,accounting for 99.82%of the SSRs,whereas motifs with>16 repeats were rare(5.79%).The repetition of sequences also varied.Sixty-nine SSR motifs were identified,including two mono-,four di-,10 tri-,24tetra-,18 penta-,and 11 hexanucleotide repeating units(Table S3).The dominant motif identified in the SSRs was A/T(18,358;62.54%),followed by AG/CT(2804;9.55%),AAG/CTT(1396;4.76%),AT/AT(1390;4.73%),AAT/ATT(1075;3.66%),ATC/ATG(725;2.47%)and AC/GT(720;2.45%).The remaining62 motifs were relatively rare,accounting for only 9.84%of the total number of SSRs(Fig.1).
| 图表编号 | XD0012317200 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2018.04.01 |
| 作者 | Houmiao Wang、Yong Lei、Liying Yan、Liyun Wan、Yan Cai、Zefeng Yang、Jianwei Lv、Xiaojie Zhang、Chenwu Xu、Boshou Liao |
| 绘制单位 | Key Laboratory of Oil Crop Biology of the Ministry of Agriculture, CAAS-ICRISAT Joint Laboratory for Groundnut Aflatoxin Management, Oil Crops Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences、Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Crop Genetics and Physi |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |