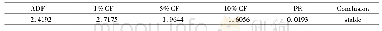《Table 6 Estimated Ccontent of shoot residue, root residue, organic manure and soil Cinput, and seed
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《Carbon cycle in response to residue management and fertilizer application in a cotton field in arid Northwest China》
The SOC and its labile fractions were significantly greater in NPK+OM than in NPK(P<0.05)(Table 5) .One reason is the readily metabolizable C and N in organic manure increased SOC by promoting plant growth,especially root growth and the production of root exudates(Bhattacharyya et al.2011).Besides,the C/N ratio in NPK+OM is appropriate for organic material decomposing(Zhang et al.2012),but the C/N in NPK is low as result of decreased the activity of microorganisms(Xu et al.2014).In our study,NPK significantly increased SOC.This finding contradicted Zhang et al.(2012),who reported that NPK had no effect on SOC in a paddy soil in Jiangxi Province,China.The NPK increased crop production and the return of crop residues and root-related C in both locations.However,SOC concentrations are relatively high in Jiangxi,and the effect of additional C inputs is small.In contrast,SOC concentrations in Xinjiang are relatively low,and additional C input causes SOC to increase.Soil C loss is also reduced by low temperatures during winter in Xinjiang(Fig.3).Bhattacharyya et al.(2011)and Zheng et al.(2015)observed that climate significantly affects the geographic distribution of SOC.The change of organic C fractions were faster than SOC(Table 5)during the growing seasons,indicated that labile organic C fractions were more sensitive to changes in soil quality.This agrees with many studies which indicate that labile SOC fractions are early indicators of changes in soil quality(Blair et al.1995;Mandal et al.2013;Zhu et al.2015).
| 图表编号 | XD0062231100 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.05.20 |
| 作者 | ZHANG Peng-peng、XU Shou-zhen、ZHANG Guo-juan、PU Xiao-zhen、WANG Jin、ZHANG Wang-feng |
| 绘制单位 | The Key Laboratory of Oasis Eco-agriculture, Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps, Agricultural College, Shihezi University、The Key Laboratory of Oasis Eco-agriculture, Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps, Agricultural College, Shihezi Univer |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |