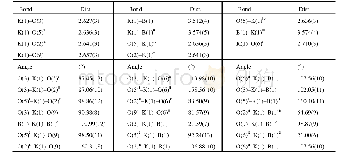
《Table 6–S-IIPs and NIPs selectivity results.》
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《"Carboxymethyl cellulose thiol-imprinted polymers:Synthesis, characterization and selective Hg(Ⅱ) adsorption"》
When an adsorbent is non-selective its adsorption capacity towards the specific ion dramatically decreases when other ions with similar charge,size or shape are present because of the competition for the active site of adsorbent that arises.Thus,a selectivity study of Hg was carried out in the presence of other divalent cations and results thereof are presented in Table 6.S-IIPs were found to possess the largest distribution coefficient for Hg(II),which indicates that the polymer still possessed high adsorption for the cation.Obviously,the selectivity coefficient of S-IIPs is higher than that of NIPs,thus pointing to the effectiveness of the imprinting process.The highest S-IIPs selectivity coefficient was observed for Pb cations,which has an ionic radius of 120 pm.The lowest selectivity coefficient was found for Co(ionic radius is 69 pm).It appears that Co ions which have the smallest ionic radii of all the ions,easily fits into Hg cavities while Pb ions possess the largest ionic radii and are as a result too large for the predefined cavities.
| 图表编号 | XD0052061600 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.05.15 |
| 作者 | Tarisai Velempini、Kriveshini Pillay、Xavier Y.MbiANDa、Omotayo A.Arotiba |
| 绘制单位 | Department of Applied Chemistry, University of Johannesburg, Doornfontein Campus、Department of Applied Chemistry, University of Johannesburg, Doornfontein Campus、Centre for Nanomaterials, University of Johannesburg, Doornfontein Campus、Department of Scien |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |