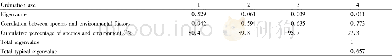
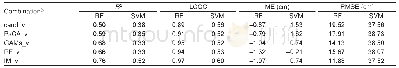
《Table 4 Summary statistics of differences of the predicted soil depth between the integrated method
 提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
提示:宽带有限、当前游客访问压缩模式
本系列图表出处文件名:随高清版一同展现
《An integrated method of selecting environmental covariates for predictive soil depth mapping》
1) IM-PG represents the difference between the IM and pedogenetic knowledge(PG)method;IM-PsCA represents the difference between IM and Pearson correlation analysis(PsCA);IM-GAMs represents the difference between IM and generalized additive models (GAMs
Fig.5 displays the differences in the prediction of regional and local distributions between the integrated method and the other variable selection methods.Table 4 summarizes the basic statistics of the differences in soil depth produced by the combinations of covariates from the integrated method and the other methods(PG,PsCA,GAMs and RF).As shown in Fig.5 and Table 4,the integrated method and the pedogenetic knowledge method had the most significant differences in the prediction results(Fig.5-A).The differences greater than 20 cm were mainly located in areas with relatively large topographic variations(such as piedmont floodplains and mountain ridges)along the river valleys in the southeastern part of the study area as well as in areas of relatively high elevations in the northwestern part of the study area,whereas the differences less than10 cm were mainly located in relatively low alluvial-diluvial plains with gentle slopes as well as in glacier-covered areas.Similar spatial distributions of the differences occurred between the integrated method and the PsCA and GAMs methods(Fig.5-B and C);the differences were less than10 cm over most of the study area,and the differences greater than 20 cm occurred occasionally in mountain ridge areas with extremely steep terrain.Compared with the PsCA and GAMs methods,the differences between the integrated method and RF method were less than 10 cm in most of the study area(Fig.5-D),and the differences greater than20 cm are mainly located in the relatively steep areas at high elevations in the arid northwestern part of the study area and in the floodplains in the river valleys.
| 图表编号 | XD0047431100 严禁用于非法目的 |
|---|---|
| 绘制时间 | 2019.02.20 |
| 作者 | LU Yuan-yuan、LIU Feng、ZHAO Yu-guo、SONG Xiao-dong、ZHANG Gan-lin |
| 绘制单位 | State Key Laboratory of Soil and Sustainable Agriculture, Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences、University of Chinese Academy of Sciences、State Key Laboratory of Soil and Sustainable Agriculture, Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy |
| 更多格式 | 高清、无水印(增值服务) |
查看“Table 4 Summary statistics of differences of the predicted soil depth between the integrated method (IM) and the convent”的人还看了
-
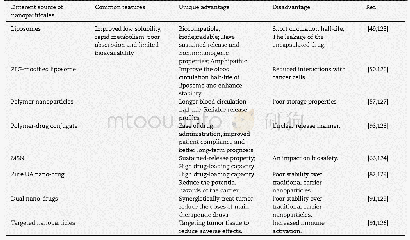
- Table 5–Summary of the differences,advantages,and disadvantages of different type nanosystems of UA in cancer therapy.